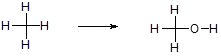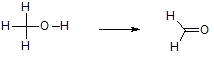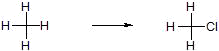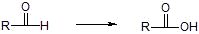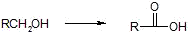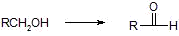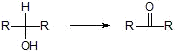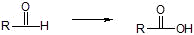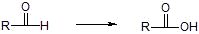1. Theoretical definition of oxidation
a) Loss of e-
b) Increase in oxidation number
Fe2+ -> Fe3+ + e-
2. Easy identification of oxidation in organic chemistry:
a) Insertion of O into a bond
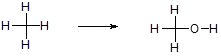
b) Loss of H2 across a bond
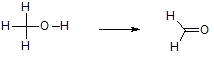
c) Replacement of H with a more electronegative element
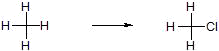
3. Determining oxidation states of C in organic molecules
a) must be done for the reactive carbon center.
b) H is always +1
c) O is -1 for each bond to C thus C-O-H is -1, C=O is -2.
4. General oxidation restrictions
a) primary alcohols
i) Jones reagent -CrO3/H+, Cr2O72-/H+,H2CrO4
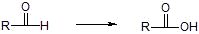
ii) KMnO4/OH-,H+
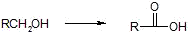
iii) Collins reagent CrO3/pyridine
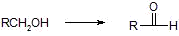
b) Secondary alcohols
i) Jones' reagent and Collins' reagent and KMnO4/OH-,H+
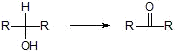
c) Tertiary alcohols
i) not easily oxidized
d) Aldehydes
i) Tollins reagent Ag(NH3)2+, H+
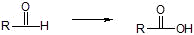
ii) KMnO4/OH-, H+
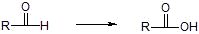
5. The mechanism of the Jones oxidation.
6. Sublimation
a) Method of purifying a volatile solid.
b) Increase mean free path of molecules. Move further without bumping into each other. Volatiles hit the cold finger first.