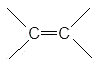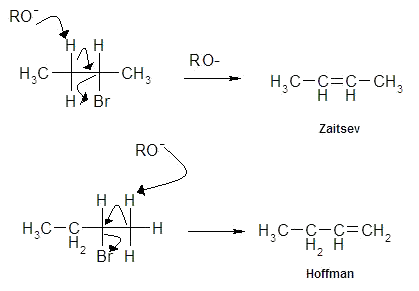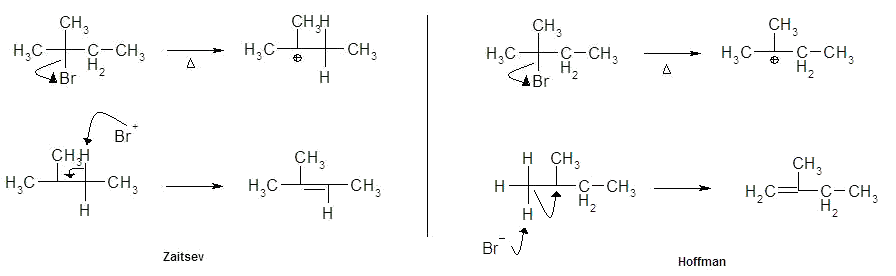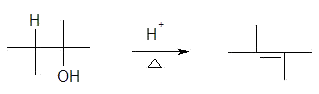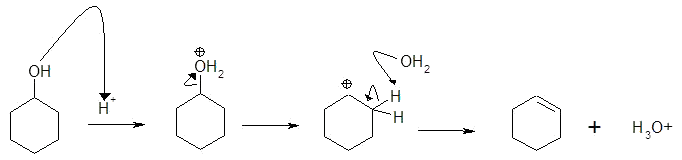1. The alkene functional group
a)
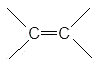
b) Csp2 σ bond, Cp-Cp π bond
2. Synthesis of alkenes
a) two elimination reactions
b) removal of hydrogen α to a good leaving group
c) two common mechanisms E1 and E2
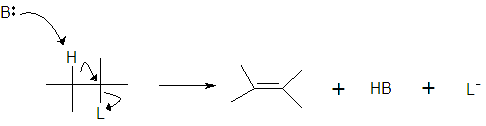
3. The E-2 Reaction
a)
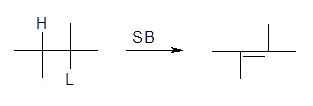
b) rate = k[R][B]
i) concerted reaction
ii) bimolecular
c) substrate
i) 3° > 2° > 1°
d) base
i) strong > weak
ii) -OH, -OR
e) need a good leaving group
f) mechanism
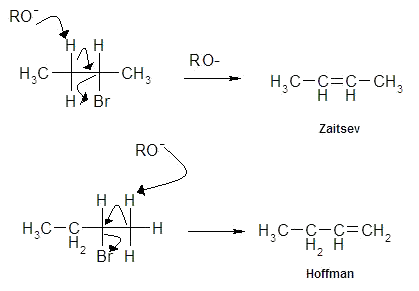
i) product ratios (Z > H)
ii) why?
a) thermodynamics
b) electronic
iii) increase H
a) large, bulky base
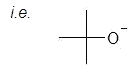
g) competition with SN2
4. The E-1 Reaction
a)

b) rate = k[RL]
i) 2 steps
ii) rds = carbocation formation
iii) unimolecular
c) substrate
i) 3° > 2° >> 1°
ii) C+ formation
d) base
i) generally weak base
ii) H2O, ROH
e) leaving group
i) need a good LG
ii) conversion of poor -> good
f) mechanism
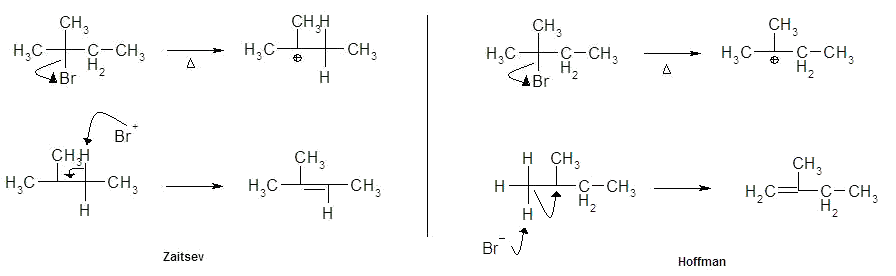
i) product ration (Z < H)
g) completion with SN1
i) increase & E1 by adding heat
5. The dehydration of alcohols
a) the reaction
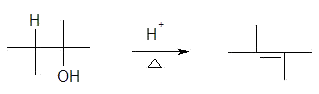
b) mechanism
i) based on substrate
a) primary - E2
b) 2°, 3° - E1
c) within cyclohexanol
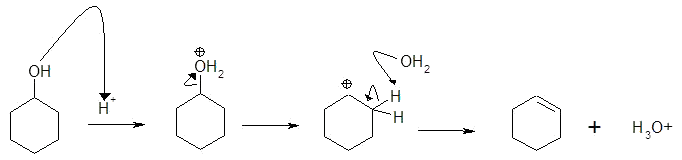
1) note acid catalyst
2) conversion of poor LG (OH) into good LG (H2O)
3) regeneration of catalyst (H3O+)