
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Geologists like igneous textures because they reveal so much about how a rock formed. The first set of textures focuses on the size of mineral crystals. Crystal size primarily reflects the rate of cooling, but is also often strongly affected by rock composition (especially water or gas content). Both intrusive and extrusive rock textures are represented.
The second set of textures is associated with volcanic rocks. Explosive volcanism creates highly distinctive features in igneous rocks. |
| 1. Textural Terms Based On Crystal Size | |||
| Intrusive Textures | Extrusive Textures | ||
|
Slow cooling |
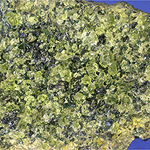 |
Fast cooling |
 |
|
Two phases of cooling: |
 |
Two phases of cooling: |
 |
|
Slow cooling plus high water content |
 |
Fast cooling plus high silica content |
 |
| 2. Volcanic Textures | ||||
|
Bubble formation with relatively low gas content |
 |
Rock foam (lots of bubbles!) |
 |
|
|
Explosive eruptive debris (tuffs and volcanic breccias) |
 |
|
 |
|
Return Home
|
|
|