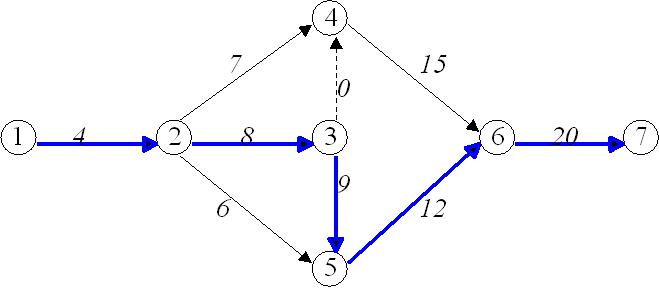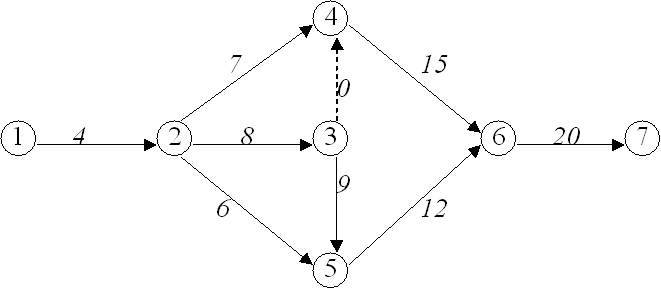

Proceeding from Node 1 to Node 7 in the forward
pass yields
the ES values, and then proceeding from Node 7 to Node 1 in the
backward
pass yields the LC values in the table below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min{LC2-D12}
= Min{4-4}=0 |
|
|
Max{ES1+D12}
= 0+4=4 |
Min{LC3-D23,LC4-D24,LC5-D25}
= Min{12-8,18-7, 21-6}=4 |
|
|
Max{ES2+D23}
=4+8=12 |
Min{LC4-D34,
LC5-D35}
Min{18-0, 21-9}=12 |
|
|
Max{ES2+D24,ES3+D34}
= Max{4+7, 12+0}=12 |
Min{LC6-D46}
= Min{33-15}=18 |
|
|
Max{ES2+D25,ES3+D35}
= Max{4+6, 12+9}=21 |
Min{LC6-D56}
= Min{33-12}=21 |
|
|
Max{ES4+D46,ES5+D56}
=Max{12+15,21+12}=33 |
Min{LC7-D67}
= Min{53-20}=33 |
|
|
Max{ES6+D67 }
=33+20 = 53 |
=ES7
= 53 |
We now go to Steps 3 and 4 to find ES, LC and TF values for each activity...
|
(i-j) |
|
|
(=LCj) |
(=LCij-ESij-Dij) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The critical activities are 1-2, 2-3, 3-5, 5-6
and 6-7
and the critical path is shown below: