| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |review |
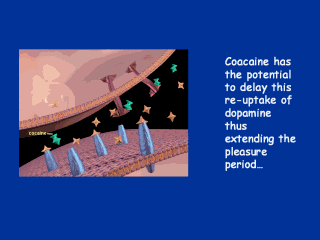 |
Cocaine and Neurotransmission Drugs of abuse are able to interfere with this normal communication process in the brain. Cocaine, for example, blocks the removal of dopamine from the synapse by binding to the dopamine transporters. As shown in this slide, this results in a buildup of dopamine in the synapse. In turn, this causes a continuous stimulation of receiving neurons, probably responsible for the euphoria reported by cocaine abusers. |