| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |review |
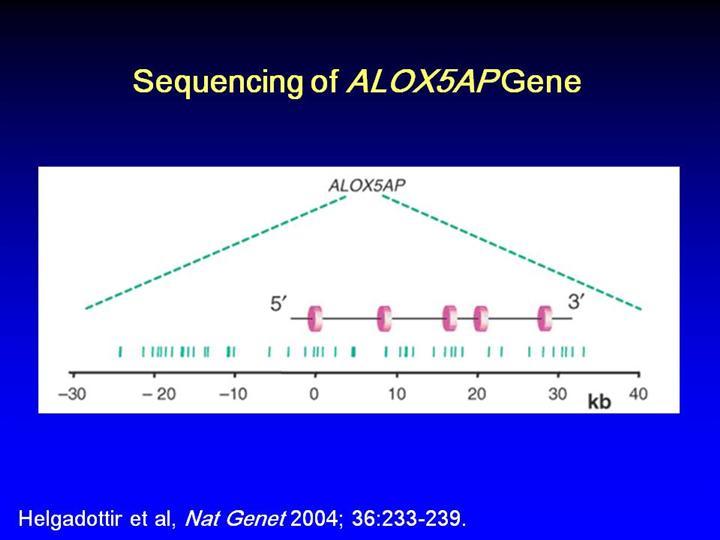 |
•144
SNPs identified in 93 cases and 93 controls, excluded 96 from further
analysis due to low MAF or complete correlation with other SNPs
•48
SNPs chose for genotyping, only one in coding region (exon 2) and was
synonymous
•Several
haplotypes were significantly associated with the disease at an adjusted
significance level of
P
< 0.05 (Supplementary
Table 5 online). We observed the most significant association with a
four-SNP haplotype spanning 33 kb, including the first four exons of
ALOX5AP
(Fig. 1c), with a nominal
P
value of 0.0000023 and an adjusted
P
value of 0.005. This haplotype, called HapA, has a haplotype frequency
of 15.8% (carrier frequency 29.1%) in affected individuals versus 9.5%
(carrier frequency 18.1%) in controls (Table 1).
|