| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |review |
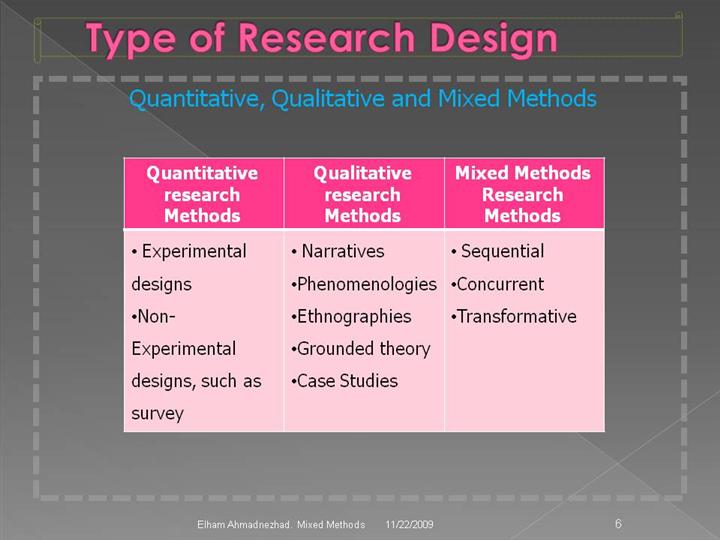 |
Strategies Associated with the quantitative approach:
•
Experiments:
include true experiments, with the random assignment of subjects to
treatment conditions.
•
Surveys:
include cross- sectional and longitudinal studies using questionnaires
or structured interviews for data collection, with the intent of
generalizing from a sample to a population.
Strategies Associated with the qualitative approach:
•
Narrative research:
a form of inquiry in with the researcher studies the lives of
individuals and asks one or more individuals to provide stories about
their lives. This information is then retold or restoried by the
researcher into narrative chronology. In the end, the narrative combines
views from the participant’s life with those of the researcher’s life in
a collaborative narrative.
•
Phenomenological research:
in which the researcher identifies the “essence” of human experiences
concerning a phenomenon, as described by participants in a study.
Understanding the “lived experiences” marks phenomenology as a
philosophy as well as a method, and the procedure involves studying a
small number of subjects through extensive and prolonged engagement to
develop patterns and relationships of meaning. In this process, the
researcher “brackets” his or her own experiences in order to understand
those of the participants in the study.
•
Ethnographies:
in which the researcher studies an intact cultural group in a natural
setting over a prolonged period of time by collecting, primarily,
observational data. The research process is flexible and typically
evolves contextually in response to the lived realities encountered in
the field setting.
•
Grounded theory:
in which the researcher attempts to derive a general, abstract theory of
a process, action, or interaction grounded in the views of participants
in a study. This process involves using multiple stages of data
collection and the refinement and interrelationship of categories of
information. Two primary characteristics of this design are the constant
comparison of data with emerging categories and theoretical sampling of
different groups to maximize the similarities and the differences of
information.
•
Case studies:
in which the researcher explores in depth a program, an event, an
activity, a process, or one or more individuals. The case(s) are bounded
by time and activity, and researchers collect detailed information using
a variety of data collection procedures over a sustained period of
time.
Strategies Associated with the mixed methods approach:
•
Sequential procedures:
in which the researcher seeks to elaborate on or expand the findings of
one method with another method. This may involve beginning with a
qualitative method for exploratory purposes and following up with a
quantitative method with a large sample so that the researcher can
generalize results to a population. Alternatively, the study may begin
with a quantitative method in which theories or concepts are tested, to
be followed by a qualitative method involving detailed exploration with
a few cases or individuals.
•
Concurrent procedures:
in which the researcher converges quantitative and qualitative data in
order to provide a comprehensive analysis of the research problem. In
this design, the investigator collects both forms of data at the same
time during the study and then integrates the information in the
interpretation of the overall results. Also, in this design, the
researcher nests one form of data within another, larger data collection
procedure in order to analyze different questions or levels of units in
an organization.
•Transformative
procedures:
in which the researcher uses a theoretical lens as in overarching
perspective within a design that contains both quantitative and
qualitative data. This lens provides a framework for topics of interest,
methods for collecting data, and outcomes or changes anticipated by the
study. Within this lens could be data collection method that involves a
sequential or a concurrent approach.
|