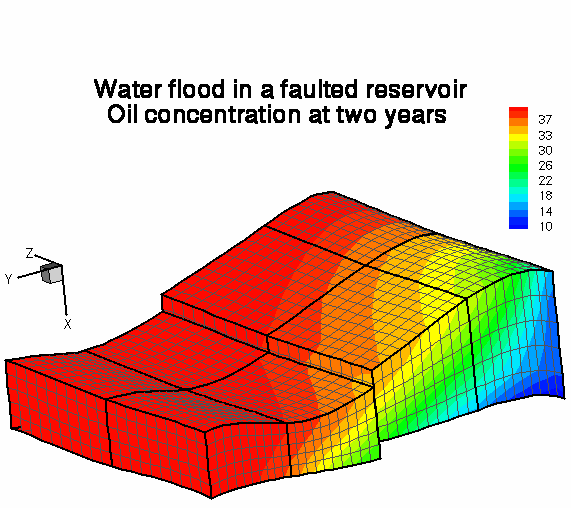
Accurate modeling of large scale geological irregularities, such as faults, layers, and fractures, is crucial for the overall accuracy of the reservoir simulation. Usually the numerical grids follow the layers, which are discontinuous across faults. Therefore it is desirable to allow for non-matching grids across interior interfaces.
The parallel two-phase flow simulator UT-MB, developed at the Center for Subsurface Modeling, simulates flow in irregularly shaped multiblock reservoirs. Each block is discretized by a locally mass conservative mixed finite element method on a logically rectangular grid. The grids may be non-matching across the interfaces. Mortar finite elements are used to impose flux continuity between blocks. The resulting procedure is highly accurate.
Click here to view a simulation of water flood in a faulted layered reservoir.
