| The Michael Group University of Pittsburgh |
|---|
|
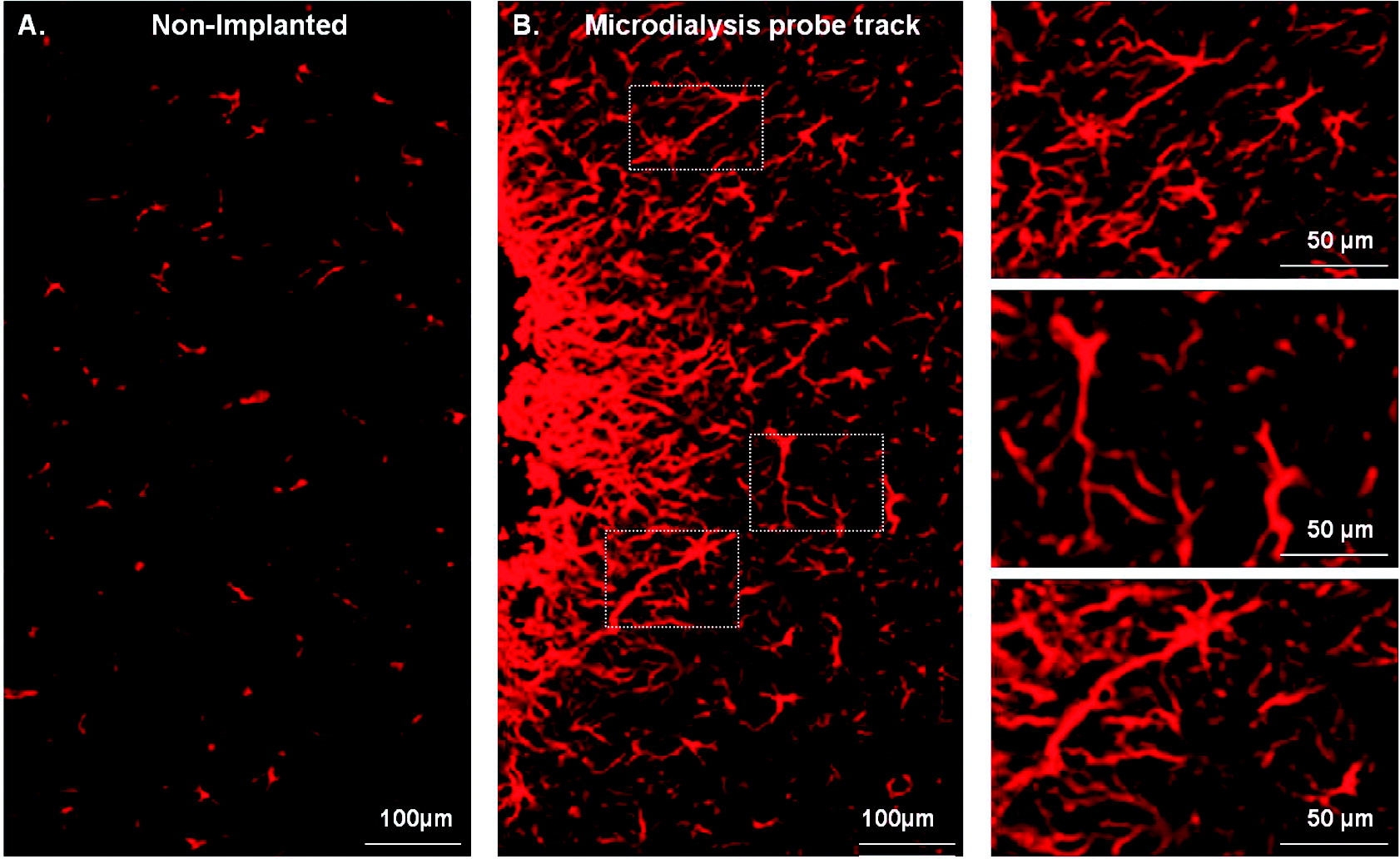
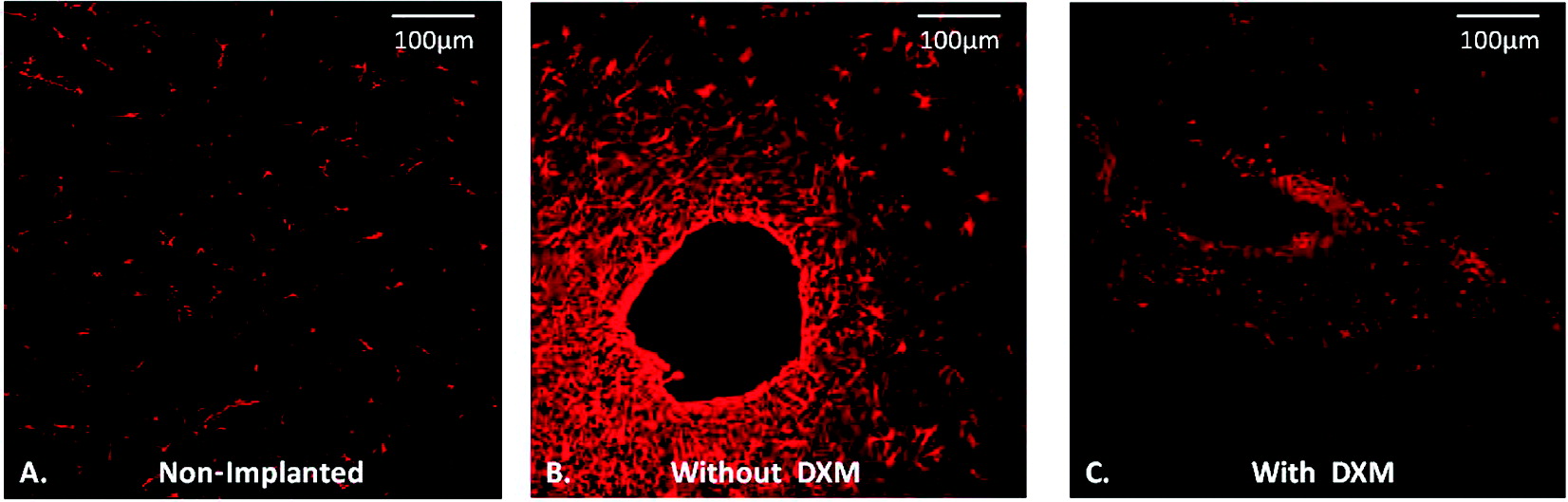
Effect of Dexamethasone on Gliosis, Ischemia, and Dopamine Extraction during Mirodialysis Sampling in Brain Tissue Microdialysis sampling of the brain is an analytical technique with numerous applications in neuroscience and the neurointensive care of brain-injured human patients. Even so, implanting microdialysis probes into brain tissue causes a penetration injury that triggers gliosis (the activation and proliferation of glial cells) and ischemia (the interruption of blood flow). Thus, the probe samples injured tissue. Mitigating the effects of the penetration injury might refine the technique. The synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone is a potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant substance. We performed microdialysis in the rat brain for 5 days, with and without dexamethasone in the perfusion fluid (10 μM for the first 24 h and 2 μM thereafter). On the first and fourth day of the perfusion, we performed dopamine no-net-flux measurements. On the fifth day, we sectioned and stained the brain tissue and examined it by fluorescence microscopy. Although dexamethasone profoundly inhibited gliosis and ischemia around the probe tracks it had only modest effects on dopamine no-net-flux results. These findings show that dexamethasone is highly effective at suppressing gliosis and ischemia but is limited in its neuroprotective activity.
| |||||||
 .
.