 University of Pittsburgh · School
of Arts and Sciences
University of Pittsburgh · School
of Arts and Sciences
Department of
History and Philosophy of Science
Graduate Program
Overview & Requirements
Areas of Concentration
Admissions
Graduate Handbook
Placement Record
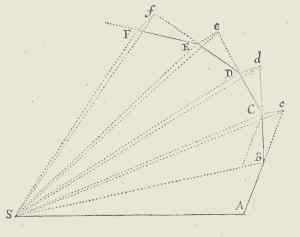 Proposition I
Proposition I
Newton's Principia
Special Program in Early Modern Philosophy and Science:
The early modern period stretches roughly from the 15th through the mid-18th century. This period includes the scientific revolution and the birth of modern philosophy and also significant transformations in mathematics, mechanics, optics, astronomy, chemistry, biology, and medicine. It also sees the rise of probabilistic reasoning, the emergence of new views of objectivity, metaphysics and epistemology, and witnesses deep changes in the wider culture of Western civilization.
This program offers the possibility of examining the theory and practice of early modern forms of cognition, the aftermath and re-orientations brought by crises and reformations in religion, the creation of democratic governments and the rise of the nation state, the emergence of new genres in literature, painting and music, the institution of capitalism, the establishment of humanism, the introduction of new technologies, legal and educational reforms, and new causes and ways of warfare. In short, one may study contextually the nature and roles of philosophy and science as they played their part in the birth of the modern world.
The program in early modern science and philosophy is intended to allow students interested in this period to develop their talents through a wide variety of seminars, informal discussions, and the availability of research materials. Students must still fulfill all HPS requirements.
The department is able to offer a generous package of financial support to most successful applicants for admission and and has an excellent record of placing its PhD graduates in academic positions.
Participating Faculty:
Peter Machamer, HPS. Galileo, Descartes and other early modern figures; epistemological, metaphysical, scientific and mathematical traditions and changes through the Enlightenment.
James Lennox, HPS. Aristotle's natural philosophy (especially biology) and philosophy of science; Galileo, Robert Boyle, William Harvey and Spinoza; the School of Medicine and Philosophy at Padua in the 16th Century and its Aristotelianism.
J.E.McGuire, HPS. Newton, Leibniz, Descartes and other early modern figures; interactions between science, philosophy and society in the 17th and 18th centuries; the scientific revolution and its historical background; the rise of the individual and new forms of cognition in the early modern period
Paolo Palmieri, HPS. Sixteenth- and seventeenth-century Aristotelian natural philosophy, Renaissance and early modern mathematics, atomism, the mathematization of nature, Galileo and the Galilean school, Newton's mechanics, and rational mechanics in the late seventeenth- and early eighteenth-century.
Joe Camp, Philosophy. Descartes and the empiricists
Stephen Engstrom, Philosophy. metaphysics, epistemology, and ethics, with a focus on Kant, and other modern philosophers, including Descartes, Leibniz, and Hume.
Kathryn Flannery, English. literacy studies, early modern British cultural studies, and women's studies. Her publications include The Emperor's New Clothes: Literature, Literacy and the Ideology of Style (1995), and articles on the intersection of gender and literacy, performance pedagogy, curriculum reform, teacher education, and the teaching of writing.
Bernard Goldstein, HPS. and Religious Studies, University Professor, emeritus History of astronomy and the other exact sciences, science and religion in the early modern period
Janelle Greenberg, History. She studies medieval and early modern political and legal institutions of England and the European continent, concentrating in particular on the growth of common law, canon law, and Roman law as well as representative government.
Ann Sutherland Harris, History of Art and Architecture. Italian 17th-century painting and sculpture (Annibale Carracci and his circle, G. L. Bernini's drawings and their role in Bernini's production; artists' education and the role of academies; art theory and practice); gender issues (women artists; images of women in 16th to 18th century art); French 17th-century painting (Simon Vouet, Nicolas Poussin, Claude Lorrain and landscape painting). I have just completed a survey text on 17th Century European Art and Architecture (Britain, the Dutch republic, the Spanish Netherlands, France, Spain and Italy) for Lawrence King, London (for 8/2004).
Kimberly Latta, English. Seventeenth- and eighteenth-century literature, economics and religion, especially Milton, Locke, Defoe, Swift, Finch, Bradstreet, Bunyan, Rochester and Behn; Marxist and feminist philosophy; theories of creation, procreation, and generation in pre-Enlightenment thought.
Dennis Looney, Italian. classical tradition in European literary culture, with a focus on the relationship between Italian vernacular culture and classical culture; Renaissance Humanism; Dante (and his reception), Petrarch, Boiardo, Ariosto, Tasso; scientific discourse in Italian literature; "cultura scritta" from writing to print.
Kenneth Manders, Philosophy. Descartes, and 17th-century mathematics.
Nicholas Rescher, University Professor of Philosophy. Leibniz and his intellectual and social context; early modern philosophy.
Kellie Robertson, English. Geoffrey of Monmouth, Chaucer, Milton, postcolonial theory, and is currently finishing a book entitled The Laborer's Two Bodies: Literary and Legal Productions, 1350-1500 (forthcoming, Palgrave). Medieval labor history as well as medieval and early modern literature, and nineteenth- and twentieth-century intellectual history.
Jonathan Scott, Carroll Admundson Professor of British History. Early modern British history in European contexts (in particular the impact upon English development of the United Provinces); the history of political thought from Plato to the Enlightenment; English republicanism; perceptions of the physical environment (especially land and sea) and their relationship to national self-perception.
Adam Shear, Religious Studies. Jewish intellectual and cultural history, particularly in early modern Italy and Western and Central Europe; the history of Jewish-Christian relations, the history of reading and writing and the transmission of learning in early modern Europe; the status of canonical and classical works in particular communities and their role in the formation of intellectual, cultural, and religious identities.
John Twyning, English. Epistemological connections between English literature, landscape and architecture: English drama & Dutch painting; London underworlds; politics and poetics in England as Arcady; the Protestant princess in her place.
Daniel Russell, French. Founding co-editor, Emblematica; 16th-centuryFrench cultural and intellectual history; emblem studies; emblems and natural history; optics and anthropomorphosis.