| Anemias might represen bone marrow failure
as a primary disorder or as a result of drug or toxin
action. Three disorders include aplastic anemia, pure red
cell aplasia, marrow replacement with fibrotic tissue or
tumor and anemias secondary to cancer. Tow mechanisms
have been postulated for aplastic anemia: Immunologic
suppression of hematopoiwsis and damage to marrow stem
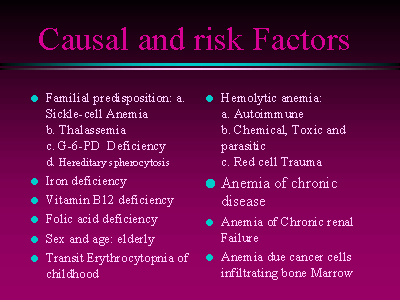
cells. Iron deficiency anemia is a sign of underlying
disease in itself. The major cause for iron deficiency in
adults is blood loss (GI bleeding in men and GY bleeding
in women), whereas in growing children and pregnant women
dietary iron lack is more common. Malabsorption also can
lead to iron deficiency. Megaloblastic anemia are anemias
in which DNA synthesis is impaired, leading to delayed
division of all rapidly proliferating cells including
hematopoietic cell. The major cause of Megaloblastic
anemia are folic acid or vitamin B12 deficiency. Acquired
hemolytic disorders is causing anemia as red cell life
span can become shortened in the course of infectious,
malignant, cardiovascular, or immunologic diseases,. In
most of these, hemolysis results from an extracorporeal
abnormality such as related hemodynamics, antibody
against red cell antigens, or exposure to toxins.
Hemoglobinopathes is abnormal hemoglobins clinically
presented with anemia and other symptoms. Sickle cell
anemia, Unstable hemoglobin and Hemoglobin of altered
oxygen affinity are resulting from abnormality in
hemoglobin structure and function. Hemolytic anemia in
Thalassemias result from mutation that affect globin
synthesis in which hemoglobin that produced is less than
normal in amount but structurally normal. Finally anemia
can be caused due hemolysis resulting from red cell
trauma. Red cell exposed to excessive mechanical stress
interavascularly or during extracorporeal circulation can
undergo fragmentation hemolysis
|