| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |review |
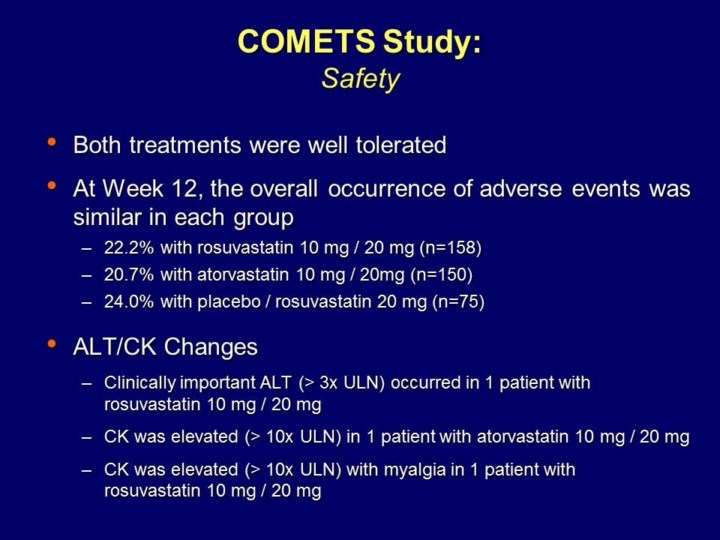 |
Both rosuvastatin 10/20 mg and atorvastatin 10/20 mg were well tolerated, with a similar incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events. The most common AEs at 6 weeks were headache, back pain, and myalgia and the most common AEs at 12 weeks were myalgia, arthralgia, and back pain. The majority of AEs were of a mild-to-moderate intensity.1
There were no reported cases of rhabdomyolysis or acute renal failure. Clinically important elevations in alanine aminotransferase (>3x ULN) occurred in one patient (rosuvastatin 10/20 mg). One patient in the atorvastatin 10/20 mg group experienced CK >10 ULN without muscle symptoms and myalgia was associated with CK>10xULN in one patient in the rosuvastatin 10/20 mg group, which was indicative of myopathy.1
Reference 1. Stalenhoef AFH et al. A COmparative study with rosuvastatin in subjects with METabolic Syndrome: results of the COMETS study. Eur Heart J. 2005;26: 2664–2672
|