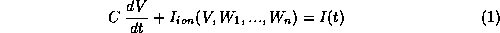
Most models for excitable membrane retain the general Hodgkin-Huxley (HH) format [20], and can be written in the form:
where V denotes membrane potential (say, deviation from a
reference, or ``rest'' level), C is membrane capacity, and 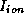 is the
sum of V- and t-dependent currents
through the various ionic channel types;
is the
sum of V- and t-dependent currents
through the various ionic channel types; 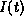 is the applied current.
The variables
is the applied current.
The variables 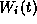 are used to describe the fraction of
channels of a given type which are in various conducting
states (e.g., open or closed
or ...) at time t. The first-order kinetics for
are used to describe the fraction of
channels of a given type which are in various conducting
states (e.g., open or closed
or ...) at time t. The first-order kinetics for 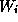 typically involve
V-dependence in the time constant
typically involve
V-dependence in the time constant 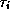 ;
; 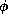 is a
temperature-like, time scale factor which may depend on i.
If the current,
is a
temperature-like, time scale factor which may depend on i.
If the current, 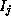 , for channel type j may be suitably
modelled as ohmic, then it might be expressed as
, for channel type j may be suitably
modelled as ohmic, then it might be expressed as
where 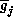 is the total conductance with all j-type channels
open
(product of single channel conductance with the total number of j-channels),
is the total conductance with all j-type channels
open
(product of single channel conductance with the total number of j-channels),
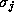 is the fraction of j-channels that are open (It may depend on
several of the variables
is the fraction of j-channels that are open (It may depend on
several of the variables 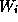 ), and
), and 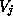 is the reversal
potential (usually Nernstian) for this ion species. For some channel types
the current-voltage relation may be more appropriately represented by the
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz expression,
or by a barrier-kinetics scheme [18], and the gating
kinetics might involve a multi-state Markov description. In the classical
HH model [20] for squid
giant axon, there are three variables
is the reversal
potential (usually Nernstian) for this ion species. For some channel types
the current-voltage relation may be more appropriately represented by the
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz expression,
or by a barrier-kinetics scheme [18], and the gating
kinetics might involve a multi-state Markov description. In the classical
HH model [20] for squid
giant axon, there are three variables 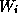 , denoted as m, h, and n, to
describe the fractions,
, denoted as m, h, and n, to
describe the fractions, 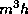 and
and 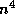 , of open
, of open 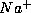 -channels
and
-channels
and 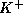 -channels, respectively.
-channels, respectively.
For some purposes, it is important that the current balance equation (1) contain terms to account for ionic pump currents. These currents, as well
as some channel conductances, may depend upon time-varying second
messengers or ionic concentrations
, e.g. in diffusionally-restricted intracellular and/or extracellular volumes.
For such considerations, additional variables and transport/kinetic balance
equations would be included in the model, and these will carry along their own
time scales. Indeed, some models that include the dynamics of intracellular
free
calcium handling have assumed time constants
which are orders of magnitude longer
than channel kinetics and thereby set the time scale for phenomena like bursting
oscillations (e.g., as in [2]). We also note that the form of
(2) is not unique; in a
phenomenological model of Rall (see [14]), the corresponding equations
are nonlinear in the 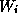 .
.
Some models for excitability contain many variables and represent numerous
channel types, especially if one seeks to account for rather detailed aspects of
spike shape and dependence upon many different pharmacological agents. On the
other hand, if qualitative or semi-quantitative characteristics of spike
generation and input-output relations are adequate, say in network simulations,
then a reduced model having just a few
variables may suffice. Such reductions can
sometimes be obtained when time scale differences allow certain approximations
such as relatively fast variables being instantaneously relaxed to
pseudo-steady-state values, e.g. if 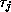 is small relative to other
time constants, then one might set
is small relative to other
time constants, then one might set 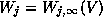 in (2).
Likewise, functionally related variables with similar time scales might be
lumped together. In this spirit, FitzHugh [10] considered reductions of
the HH model (also see [29] and [21]) and then introduced [11] an
idealized, analytically tractable,
two-variable model (also see [24]) which is widely studied as a
qualitative prototype for excitable systems in many biological/chemical
contexts.
A
FitzHugh-Nagumo/Hodgkin-Huxley hybrid was formulated and studied by Morris and
Lecar [23], in the context of electrical activity of the barnacle muscle
fiber. The model incorporates a V-gated
in (2).
Likewise, functionally related variables with similar time scales might be
lumped together. In this spirit, FitzHugh [10] considered reductions of
the HH model (also see [29] and [21]) and then introduced [11] an
idealized, analytically tractable,
two-variable model (also see [24]) which is widely studied as a
qualitative prototype for excitable systems in many biological/chemical
contexts.
A
FitzHugh-Nagumo/Hodgkin-Huxley hybrid was formulated and studied by Morris and
Lecar [23], in the context of electrical activity of the barnacle muscle
fiber. The model incorporates a V-gated 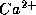 -channel and a V-gated,
delayed-rectifier,
-channel and a V-gated,
delayed-rectifier, 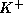 -channel; neither current inactivates. A
simple version of this model is represented by the equations:
-channel; neither current inactivates. A
simple version of this model is represented by the equations:
where
In
equations (4)-(6), w is the fraction of 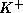 -channels open,
and
the
-channels open,
and
the 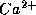 -channels respond to V so rapidly that we assume instantaneous
activation.
One might introduce dimensionless variables, as
in [31] and [12], in order
to (i) reduce the number of free parameters and identify
equivalent groups of parameters, and (ii) identify and
group ``fast" and
``slow" processes together. However, in the interest
of clarity, we will keep all equations in their original form.
In (5),
-channels respond to V so rapidly that we assume instantaneous
activation.
One might introduce dimensionless variables, as
in [31] and [12], in order
to (i) reduce the number of free parameters and identify
equivalent groups of parameters, and (ii) identify and
group ``fast" and
``slow" processes together. However, in the interest
of clarity, we will keep all equations in their original form.
In (5),
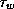 has been scaled so its maximum is now one, and
has been scaled so its maximum is now one, and 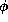 equals
the temperature factor divided by the pre-scaled maximum
(
equals
the temperature factor divided by the pre-scaled maximum
(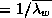 in
[23]). The V-dependent functions,
in
[23]). The V-dependent functions, 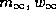 , and
, and
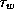 , and
the reference parameter sets are given in Appendix A.
All the computations and figures
in this chapter are based on equations (4)-(6), and
extensions of them for generating bursting behaviors.
, and
the reference parameter sets are given in Appendix A.
All the computations and figures
in this chapter are based on equations (4)-(6), and
extensions of them for generating bursting behaviors.
Even network models in certain approximations can reduce to a few variables. One example is the Wilson-Cowan model [37]: (for another, see Shamma in this volume)
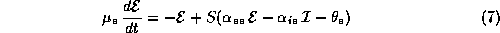

Here, 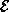 and
and 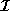 represent the respective firing rates of a
population of
excitatory and inhibitory interneurons. The parameters
represent the respective firing rates of a
population of
excitatory and inhibitory interneurons. The parameters 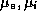 are the
membrane time constants;
are the
membrane time constants; 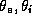 are the firing thresholds;
are the firing thresholds;
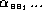 are the ``synaptic weights''; and
are the ``synaptic weights''; and 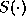 is a nonlinear
saturating function similar in form to
is a nonlinear
saturating function similar in form to 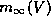 .
.