| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |review |
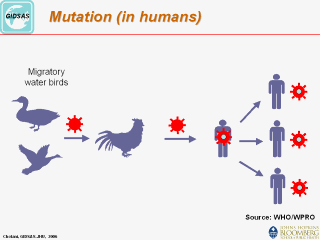 |
Mutation: In general mutations are changes to the DNA or RNA (genetic materials) of viruses. Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division and by exposure to elements such as radiation, chemicals, viruses or can occur deliberately under cellular control during the processes such as meiosis or hyper-mutation. Mutations are considered the driving force of evolution, where less favorable (or deleterious) mutations are removed from the gene pool by natural selection, while more favorable (beneficial or advantageous) ones tend to accumulate. |