 |
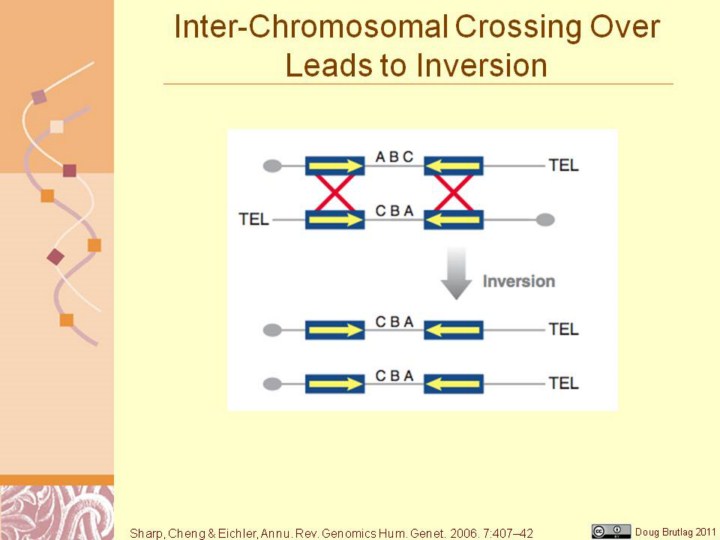
Interspersed segmental duplications provide a substrate for genomic
rearrangement via nonallelic homologous recombination (NAHR). (a and b)
Interchromosomal, intrachromosomal, or intrachromatid NAHR between directly
orientated repeats causes deletion and/or duplication of the intervening
sequence. (c and d ) Interchromosomal, intrachromosomal, or intrachromatid
NAHR between inverted repeats causes inversion of the intervening sequence.
Repeat sequences are depicted as blue boxes, with their orientation
indicated by yellow arrows, and recombination is shown by red crosses.
Adapted in part from References 40 and 63.
|
