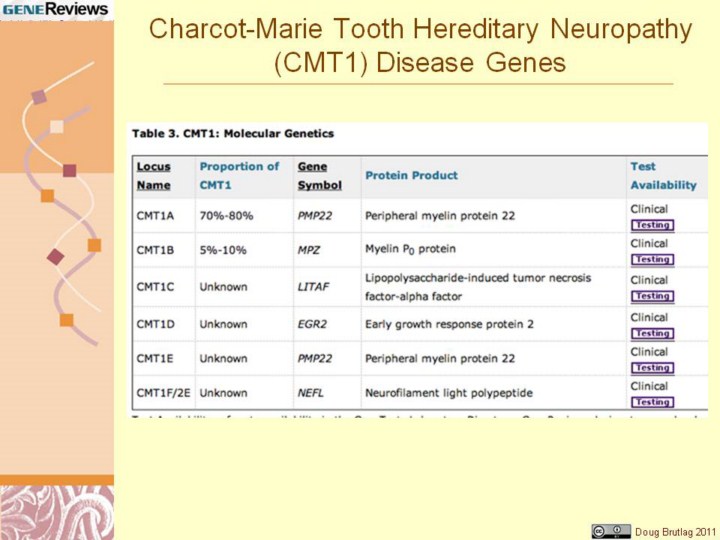
 |
n 1991,
Charcot-Marie Tooth (CMT) disease was the first autosomal dominant disease
associated with a gene dosage effect due to an inherited DNA rearrangement.
Most cases of CMT1A are associated with a 1.5-Mb tandem duplication in
17p11.2-p12, mediated by flanking segmental duplications, that encompasses
the PMP22 gene (see
Figure 1). The disease phenotype results from having three copies of the
normal gene. The reciprocal product of the recombination, a single copy of
the PMP22 gene, results in the clinically distinct hereditary neuropathy
with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP)
[3] .
|
