
Next: Semi-infinite cable
Up: The passive cable equation
Previous: The passive cable equation
To make life easier, we set E=0. The solution to (12)
depends on the initial spatial distribution of voltage and the
conditions at the ends of the cable, the boundary conditions.
We will consider either a finite cable of length l or a
semi-infinite cable where one end goes to infinity. We will first look
only at the steady state behavior of the cable. In this case, we drop
the derivative with respect to t and obtain:
| 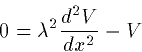 |
(12) |
whose general solution is one of the following forms:
We define the input resistance of a cable as the ratio of the
steady state potential divided by the current injected.
G. Bard Ermentrout
1/10/1998