Release 8.0
A58236-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference Release 8.0 A58236-01 |
|
Grammar, which knows how to control even kings.
Molière
This chapter is a quick reference guide to PL/SQL syntax and semantics. It shows you how commands, parameters, and other language elements are sequenced to form PL/SQL statements. Also, to save you time and trouble, it provides usage notes and short examples.
When you are unsure of the syntax to use in a PL/SQL statement, trace through its syntax diagram, reading from left to right and top to bottom. You can verify or construct any PL/SQL statement that way.
The diagrams are graphic representations of Bachus-Naur Form (BNF) productions. Within the diagrams, keywords are enclosed in boxes, delimiters in circles, and identifiers in ovals.
Each diagram defines a syntactic element. Every path through the diagram describes a possible form of that element. Follow in the direction of the arrows. If a line loops back on itself, you can repeat the element enclosed by the loop.
An assignment statement sets the current value of a variable, field, parameter, or element. The statement consists of an assignment target followed by the assignment operator and an expression. When the statement is executed, the expression is evaluated and the resulting value is stored in the target. For more information, see "Assignments".
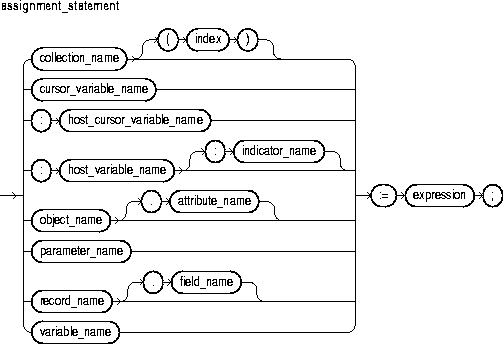
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope. Only the value of another cursor variable can be assigned to a cursor variable.
This identifies a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This identifies a variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This identifies an object (instance of an object type) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies an indicator variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL. Indicator variables must be prefixed with a colon. An indicator variable "indicates" the value or condition of its associated host variable. For example, in the Oracle Precompiler environment, indicator variables let you detect nulls or truncated values in output host variables.
This identifies a formal OUT or IN OUT parameter of the subprogram in which the assignment statement appears.
This is a numeric expression that must yield a value of type BINARY_INTEGER or a value implicitly convertible to that datatype.
This identifies a field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL variable previously declared within the current scope.
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. For the syntax of expression, see "Expressions". When the assignment statement is executed, the expression is evaluated and the resulting value is stored in the assignment target. The value and target must have compatible datatypes.
By default, unless a variable is initialized in its declaration, it is initialized to NULL every time a block or subprogram is entered. So, never reference a variable before you assign it a value.
You cannot assign nulls to a variable defined as NOT NULL. If you try, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception VALUE_ERROR.
Only the values TRUE and FALSE and the non-value NULL can be assigned to a Boolean variable. When applied to an expression, the relational operators return a Boolean value. So, the following assignment is legal:
DECLARE out_of_range BOOLEAN; ... BEGIN ... out_of_range := (salary < minimum) OR (salary > maximum);
As the next example shows, you can assign the value of an expression to a specific field in a record:
DECLARE emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE; BEGIN ... emp_rec.sal := current_salary + increase;
Moreover, you can assign values to all fields in a record at once. PL/SQL allows aggregate assignment between entire records if their declarations refer to the same cursor or table. For example, the following assignment is legal:
DECLARE emp_rec1 emp%ROWTYPE; emp_rec2 emp%ROWTYPE; dept_rec dept%ROWTYPE; BEGIN ... emp_rec1 := emp_rec2;
The next assignment is illegal because you cannot use the assignment operator to assign a list of values to a record:
dept_rec := (60, 'PUBLICITY', 'LOS ANGELES');
Using the following syntax, you can assign the value of an expression to a specific element in a collection:
collection_name(index) := expression;
In the following example, you assign the uppercase value of last_name to the third row in nested table ename_tab:
ename_tab(3) := UPPER(last_name);
Several examples of assignment statements follow:
wages := hours_worked * hourly_salary; country := 'France'; costs := labor + supplies; done := (count > 100); dept_rec.loc := 'BOSTON'; comm_tab(5) := sales * 0.15;
Constants and Variables, Expressions, SELECT INTO Statement
The basic program unit in PL/SQL is the block. A PL/SQL block is defined by the keywords DECLARE, BEGIN, EXCEPTION, and END. These keywords partition the PL/SQL block into a declarative part, an executable part, and an exception-handling part. Only the executable part is required. You can nest a block within another block wherever you can place an executable statement. For more information, see "Block Structure" and "Scope and Visibility".
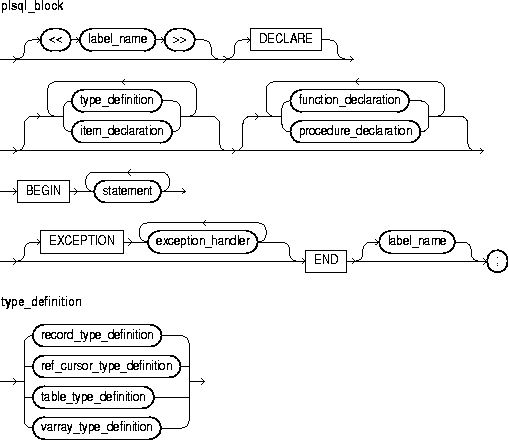


This is an undeclared identifier that optionally labels a PL/SQL block. If used, label_name must be enclosed by double angle brackets and must appear at the beginning of the block. Optionally, label_name can also appear at the end of the block.
A global identifier declared in an enclosing block can be redeclared in a sub-block, in which case the local declaration prevails and the sub-block cannot reference the global identifier. To reference the global identifier, you must use a block label to qualify the reference, as the following example shows:
<<outer>> DECLARE x INTEGER; BEGIN ... DECLARE x INTEGER; BEGIN ... IF x = outer.x THEN -- refers to global x ... END IF; END; END outer;
This keyword signals the start of the declarative part of a PL/SQL block, which contains local declarations. Items declared locally exist only within the current block and all its sub-blocks and are not visible to enclosing blocks. The declarative part of a PL/SQL block is optional. It is terminated implicitly by the keyword BEGIN, which introduces the executable part of the block.
PL/SQL does not allow forward references. So, you must declare an item before referencing it in other statements, including other declarative statements. Also, you must declare subprograms at the end of a declarative section after all other program items.
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope. For the syntax of collection_declaration, see "Collections".
This construct declares a constant. For the syntax of constant_declaration, see "Constants and Variables".
This construct declares an explicit cursor. For the syntax of cursor_declaration, see "Cursors".
This construct declares a cursor variable. For the syntax of cursor_variable_declaration, see "Cursor Variables".
This construct declares an exception. For the syntax of exception_declaration, see "Exceptions".
This identifies an object (instance of an object type) previously declared within the current scope. For the syntax of object_declaration, see "Object Types".
This construct declares a user-defined record. For the syntax of record_declaration, see "Records".
This construct declares a variable. For the syntax of variable_declaration, see "Constants and Variables".
This construct declares a function. For the syntax of function_declaration, see "Functions".
This construct declares a procedure. For the syntax of procedure_declaration, see "Procedures".
This keyword signals the start of the executable part of a PL/SQL block, which contains executable statements. The executable part of a PL/SQL block is required. That is, a block must contain at least one executable statement. The NULL statement meets this requirement.
This is an executable (not declarative) statement that you use to create algorithms. A sequence of statements can include procedural statements such as RAISE, SQL statements such as UPDATE, and PL/SQL blocks (sometimes called block statements).
PL/SQL statements are free format. That is, they can continue from line to line if you do not split keywords, delimiters, or literals across lines. A semicolon (;) serves as the statement terminator.
PL/SQL supports a subset of SQL statements that includes data manipulation, cursor control, and transaction control statements but excludes data definition and data control statements such as ALTER, CREATE, GRANT, and REVOKE.
This keyword signals the start of the exception-handling part of a PL/SQL block. When an exception is raised, normal execution of the block stops and control transfers to the appropriate exception handler. After the exception handler completes, execution proceeds with the statement following the block.
If there is no exception handler for the raised exception in the current block, control passes to the enclosing block. This process repeats until an exception handler is found or there are no more enclosing blocks. If PL/SQL can find no exception handler for the exception, execution stops and an unhandled exception error is returned to the host environment. For more information, see Chapter 6.
This construct associates an exception with a sequence of statements, which is executed when that exception is raised. For the syntax of exception_handler, see "Exceptions".
This keyword signals the end of a PL/SQL block. It must be the last keyword in a block. Neither the END IF in an IF statement nor the END LOOP in a LOOP statement can substitute for the keyword END.
END does not signal the end of a transaction. Just as a block can span multiple transactions, a transaction can span multiple blocks.
The following PL/SQL block declares several variables and constants, then calculates a ratio using values selected from a database table:
-- available online in file 'examp11' DECLARE numerator NUMBER; denominator NUMBER; the_ratio NUMBER; lower_limit CONSTANT NUMBER := 0.72; samp_num CONSTANT NUMBER := 132; BEGIN SELECT x, y INTO numerator, denominator FROM result_table WHERE sample_id = samp_num; the_ratio := numerator/denominator; IF the_ratio > lower_limit THEN INSERT INTO ratio VALUES (samp_num, the_ratio); ELSE INSERT INTO ratio VALUES (samp_num, -1); END IF; COMMIT; EXCEPTION WHEN ZERO_DIVIDE THEN INSERT INTO ratio VALUES (samp_num, 0); COMMIT; WHEN OTHERS THEN ROLLBACK; END;
Constants and Variables, Exceptions, Functions, Procedures
The CLOSE statement allows resources held by an open cursor or cursor variable to be reused. No more rows can be fetched from a closed cursor or cursor variable. For more information, see "Managing Cursors".

This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope and currently open.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable (or parameter) previously declared within the current scope and currently open.
This identifies a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
Once a cursor or cursor variable is closed, you can reopen it using the OPEN or OPEN-FOR statement, respectively. If you reopen a cursor without closing it first, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception CURSOR_ALREADY_OPEN. However, you need not close a cursor variable before reopening it.
If you try to close an already-closed or never-opened cursor or cursor variable, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception INVALID_CURSOR.
In the following example, after the last row is fetched and processed, you close the cursor variable emp_cv:
LOOP FETCH emp_cv INTO emp_rec; EXIT WHEN emp_cv%NOTFOUND; ... -- process data record END LOOP; /* Close cursor variable. */ CLOSE emp_cv;
FETCH Statement, OPEN Statement, OPEN-FOR Statement
A collection method is a built-in function or procedure that operates on collections and is called using dot notation. The methods EXISTS, COUNT, LIMIT, FIRST, LAST, PRIOR, NEXT, EXTEND, TRIM, and DELETE help generalize code, make collections easier to use, and make your applications easier to maintain.
EXISTS, COUNT, LIMIT, FIRST, LAST, PRIOR, and NEXT are functions, which appear as part of an expression. EXTEND, TRIM, and DELETE are procedures, which appear as a statement. EXISTS, PRIOR, NEXT, TRIM, EXTEND, and DELETE take integer parameters. For more information, see "Using Collection Methods".
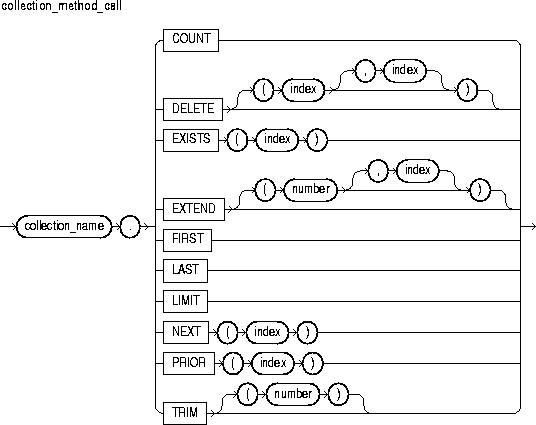
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope.
COUNT returns the number of elements that a collection currently contains, which is useful because the current size of a collection is not always known. You can use COUNT wherever an integer expression is allowed.
For varrays, COUNT always equals LAST. For nested tables, normally, COUNT equals LAST. But, if you delete elements from the middle of a nested table, COUNT is smaller than LAST.
This procedure has three forms. DELETE removes all elements from a collection. DELETE(n) removes the nth element from a nested table. If n is null, DELETE(n) does nothing. DELETE(m,n) removes all elements in the range m..n from a nested table. If m is larger than n or if m or n is null, DELETE(m,n) does nothing.
This is an expression that must yield (or convert implicitly to) an integer. For more information, see "Datatype Conversion".
EXISTS(n) returns TRUE if the nth element in a collection exists. Otherwise, EXISTS(n) returns FALSE. Mainly, you use EXISTS with DELETE to maintain sparse nested tables. You can also use EXISTS to avoid raising an exception when you reference a nonexistent element.
When passed an out-of-range subscript, EXISTS returns FALSE instead of raising SUBSCRIPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT.
This procedure has three forms. EXTEND appends one null element to a collection. EXTEND(n) appends n null elements to a collection. EXTEND(n,i) appends n copies of the ith element to a collection.
EXTEND operates on the internal size of a collection. So, if EXTEND encounters deleted elements, it includes them in its tally.
FIRST and LAST return the first and last (smallest and largest) index numbers in a collection. If the collection is empty, FIRST and LAST return NULL. If the collection contains only one element, FIRST and LAST return the same index number.
For varrays, FIRST always returns 1 and LAST always equals COUNT. For nested tables, normally, LAST equals COUNT. But, if you delete elements from the middle of a nested table, LAST is larger than COUNT.
For nested tables, which have no maximum size, LIMIT returns NULL. For varrays, LIMIT returns the maximum number of elements that a varray can contain (which you specify in its type definition).
PRIOR(n) returns the index number that precedes index n in a collection. NEXT(n) returns the index number that succeeds index n. If n has no predecessor, PRIOR(n) returns NULL. Likewise, if n has no successor, NEXT(n) returns NULL.
This procedure has two forms. TRIM removes one element from the end of a collection. TRIM(n) removes n elements from the end of a collection. If n is greater than COUNT, TRIM(n) raises SUBSCRIPT_BEYOND_COUNT.
TRIM operates on the internal size of a collection. So, if TRIM encounters deleted elements, it includes them in its tally.
You cannot use collection methods in a SQL statement. If you try, you get a compilation error.
Only EXISTS can be applied to atomically null collections. If you apply another method to such collections, PL/SQL raises COLLECTION_IS_NULL.
You can use PRIOR or NEXT to traverse collections indexed by any series of subscripts. For example, you can use PRIOR or NEXT to traverse a nested table from which some elements have been deleted.
EXTEND operates on the internal size of a collection, which includes deleted elements. You cannot use EXTEND to initialize an atomically null collection. Also, if you impose the NOT NULL constraint on a TABLE or VARRAY type, you cannot apply the first two forms of EXTEND to collections of that type.
If an element to be deleted does not exist, DELETE simply skips it; no exception is raised. Varrays are dense, so you cannot delete their individual elements.
PL/SQL keeps placeholders for deleted elements. So, you can replace a deleted element simply by assigning it a new value. However, PL/SQL does not keep placeholders for trimmed elements.
The amount of memory allocated to a nested table can increase or decrease dynamically. As you delete elements, memory is freed page by page. If you delete the entire table, all the memory is freed.
In general, do not depend on the interaction between TRIM and DELETE. It is better to treat nested tables like fixed-size arrays and use only DELETE, or to treat them like stacks and use only TRIM and EXTEND.
Within a subprogram, a collection parameter assumes the properties of the argument bound to it. So, you can apply methods FIRST, LAST, COUNT, and so on to such parameters. For varray parameters, the value of LIMIT is always derived from the parameter type definition, regardless of the parameter mode.
In the following example, you use NEXT to traverse a nested table from which some elements have been deleted:
i := courses.FIRST; -- get subscript of first element WHILE i IS NOT NULL LOOP -- do something with courses(i) i := courses.NEXT(i); -- get subscript of next element END LOOP;
In the following example, PL/SQL executes the assignment statement only if element i exists:
IF courses.EXISTS(i) THEN courses(i) := new_course; END IF;
The next example shows that you can use FIRST and LAST to specify the lower and upper bounds of a loop range provided each element in that range exists:
FOR i IN courses.FIRST..courses.LAST LOOP ...
In the following example, you delete elements 2 through 5 from a nested table:
courses.DELETE(2, 5);
In the next example, you use LIMIT to determine if you can add 20 more elements to varray projects:
IF (projects.COUNT + 20) < projects.LIMIT THEN -- add 20 more elements
Collections
A collection is an ordered group of elements, all of the same type (for example, the grades for a class of students). Each element has a unique subscript that determines its position in the collection. PL/SQL offers two kinds of collections: nested tables and varrays (short for variable-size arrays).
Collections work like the arrays found in most third-generation programming languages. However, collections can have only one dimension and must be indexed by integers. (In some languages such as Ada and Pascal, arrays can have multiple dimensions and can be indexed by enumeration types.)
Collections can store instances of an object type and, conversely, can be attributes of an object type. Also, collections can be passed as parameters. So, you can use them to move columns of data into and out of database tables or between client-side applications and stored subprograms. For more information, see "Defining and Declaring Collections".
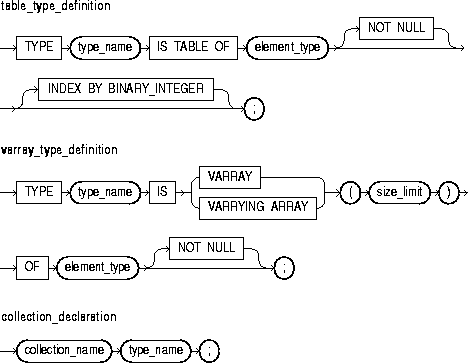
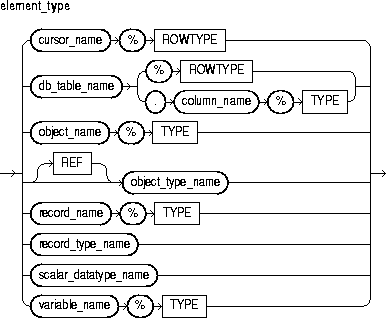
This identifies a user-defined type specifier, which is used in subsequent declarations of collections.
This is any PL/SQL datatype except BOOLEAN, NCHAR, NCLOB, NVARCHAR2, REF CURSOR, TABLE, and VARRAY, or is any object type except those with TABLE or VARRAY attributes. If element_type is a record type, every field in the record must be a scalar type or an object type.
This optional clause lets you define Version 2 PL/SQL tables, which are called index-by tables in Version 8.
This is a positive integer literal that specifies the maximum size of a varray, which is the maximum number of elements the varray can contain.
Every element reference includes the collection name and a subscript enclosed in parentheses; the subscript determines which element is processed. Except for index-by tables, collection subscripts have a fixed lower bound of 1.
Nested tables can be sparse (have non-consecutive subscripts), but varrays are always dense (have consecutive subscripts). Unlike nested tables, varrays retain their ordering and subscripts when stored in the database.
You can define collection types in the declarative part of any PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. In SQL, collection types can be CREATEd and stored in the database.
Collections follow the usual scoping and instantiation rules. In a package, collections are instantiated when you first reference the package and cease to exist when you end the database session. In a block or subprogram, local collections are instantiated when you enter the block or subprogram and cease to exist when you exit.
Until you initialize it, a collection is atomically null (that is, the collection itself is null, not its elements). To initialize a collection, you use a constructor, which is a system-defined function with the same name as the collection type. This function "constructs" a collection from the elements passed to it.
Because collections can be atomically null, they can be tested for nullity. However, collections cannot be compared for equality or inequality. This restriction also applies to implicit comparisons. For example, collections cannot appear in a DISTINCT, GROUP BY, or ORDER BY list.
Collections can store instances of an object type and, conversely, can be attributes of an object type. Also, nested tables and varrays can be passed as parameters. So, you can use them to move collections of data into and out of database tables or between client-side applications and stored subprograms.
When calling a function that returns a collection, you use the following syntax to reference elements in the collection:
collection_name(parameter_list)(subscript)
With the Oracle Call Interface (OCI) or the Oracle Precompilers, you can bind host arrays to collections declared as the formal parameters of a subprogram. That allows you to pass host arrays to stored functions and procedures.
To specify the element type of a collection, you can use %TYPE or %ROWTYPE, as the following example shows:
DECLARE TYPE JobList IS VARRAY(10) OF emp.job%TYPE; -- based on column CURSOR c1 IS SELECT * FROM dept; TYPE DeptFile IS TABLE OF c1%ROWTYPE; -- based on cursor TYPE EmpFile IS VARRAY(150) OF emp%ROWTYPE; -- based on database table
In the next example, you use a RECORD type to specify the element type:
DECLARE TYPE Entry IS RECORD ( term VARCHAR2(20), meaning VARCHAR2(200)); TYPE Glossary IS VARRAY(250) OF Entry;
When defining a VARRAY type, you must specify its maximum size. In the following example, you define a type that stores up to 366 dates:
DECLARE TYPE Calendar IS VARRAY(366) OF DATE;
Once you define a collection type, you can declare collections of that type, as the following SQL*Plus script shows:
CREATE TYPE Project AS OBJECT( project_no NUMBER(2), title VARCHAR2(35), cost NUMBER(7,2)) / CREATE TYPE ProjectList AS VARRAY(50) OF Project -- define VARRAY type / CREATE TABLE department ( idnum NUMBER(2), name VARCHAR2(15), budget NUMBER(11,2), projects ProjectList) -- declare varray /
The identifier projects represents an entire varray. Each element of projects will store a Project object.
In the following example, you declare a nested table as the formal parameter of a packaged procedure:
CREATE PACKAGE personnel AS TYPE Staff IS TABLE OF Employee; ... PROCEDURE award_bonuses (members IN Staff);
You can specify a collection type in the RETURN clause of a function specification, as the following example shows:
DECLARE TYPE SalesForce IS VARRAY(20) OF Salesperson; FUNCTION top_performers (n INTEGER) RETURN SalesForce IS ...
In the following example, you update the list of projects assigned to the Security Department:
DECLARE new_projects ProjectList := ProjectList(Project(1, 'Issue New Employee Badges', 13500), Project(2, 'Inspect Emergency Exits', 1900), Project(3, 'Upgrade Alarm System', 3350), Project(4, 'Analyze Local Crime Statistics', 825)); BEGIN UPDATE department SET projects = new_projects WHERE name = 'Security';
In the next example, you retrieve all the projects for the Accounting Department into a local varray:
DECLARE my_projects ProjectList; BEGIN SELECT projects INTO my_projects FROM department WHERE name = 'Accounting';
Collection Methods, Object Types, Records
Comments describe the purpose and use of code segments and so promote readability. PL/SQL supports two comment styles: single-line and multi-line. Single-line comments begin with a double hyphen (--) anywhere on a line and extend to the end of the line. Multi-line comments begin with a slash-asterisk (/*), end with an asterisk-slash (*/), and can span multiple lines. For more information, see "Comments".
Comments can appear within a statement at the end of a line. However, you cannot nest comments.
You cannot use single-line comments in a PL/SQL block that will be processed dynamically by an Oracle Precompiler program because end-of-line characters are ignored. As a result, single-line comments extend to the end of the block, not just to the end of a line. Instead, use multi-line comments.
While testing or debugging a program, you might want to disable a line of code. The following example shows how you can "comment-out" the line:
-- UPDATE dept SET loc = my_loc WHERE deptno = my_deptno;
You can use multi-line comment delimiters to comment-out whole sections of code.
The following examples show various comment styles:
-- compute the area of a circle area := pi * radius**2; -- pi equals 3.14159 /* Compute the area
of a circle. */ area := pi * radius**2; /* pi equals 3.14159 */
The COMMIT statement explicitly makes permanent any changes made to the database during the current transaction. Changes made to the database are not considered permanent until they are committed. A commit also makes the changes visible to other users. For more information, see "Processing Transactions".

This keyword is optional and has no effect except to improve readability.
This keyword specifies a comment to be associated with the current transaction and is typically used with distributed transactions. The text must be a quoted literal no more than 50 characters long.
The COMMIT statement releases all row and table locks. It also erases any savepoints you marked since the last commit or rollback. Until your changes are committed, the following conditions hold:
ROLLBACK statement to roll back (undo) the changes.
If you commit while a cursor that was declared using FOR UPDATE is open, a subsequent fetch on that cursor raises an exception. The cursor remains open, however, so you should close it. For more information, see "Using FOR UPDATE".
When a distributed transaction fails, the text specified by COMMENT helps you diagnose the problem. If a distributed transaction is ever in doubt, Oracle stores the text in the data dictionary along with the transaction ID. For more information about distributed transactions, see Oracle8 Concepts.
PL/SQL does not support the FORCE clause, which, in SQL, manually commits an in-doubt distributed transaction. For example, the following COMMIT statement is illegal:
COMMIT FORCE '23.51.54'; -- illegal
With embedded SQL, the optional RELEASE parameter is allowed after COMMIT WORK. The keyword RELEASE acts like a "disconnect" statement, which logs you off the database once your transaction is committed. PL/SQL does not support data control statements such as CONNECT, GRANT, or REVOKE. Therefore, it does not support the RELEASE parameter.
ROLLBACK Statement, SAVEPOINT Statement
You can declare constants and variables in the declarative part of any PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. Declarations allocate storage space for a value, specify its datatype, and name the storage location so that you can reference it. Declarations can also assign an initial value and impose the NOT NULL constraint. For more information, see "Declarations".
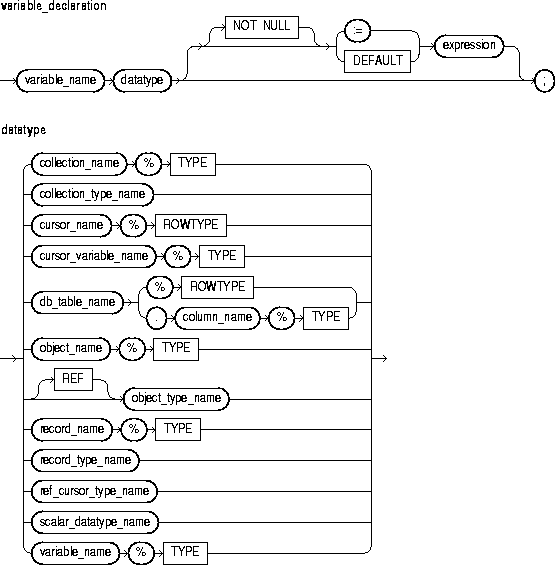
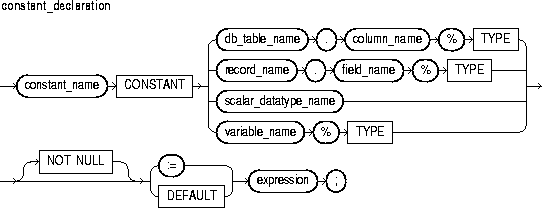
This identifies a program constant. For naming conventions, see "Identifiers".
This keyword denotes the declaration of a constant. You must initialize a constant in its declaration. Once initialized, the value of a constant cannot be changed.
This identifies a field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a predefined scalar datatype such as BOOLEAN, NUMBER, or VARCHAR2. For more information, see "Datatypes".
This identifies a database table and column that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
This identifies a program variable.
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies an object (instance of an object type) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a user-defined record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a database table (or view) that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
This attribute provides a record type that represents a row in a database table or a row fetched from a previously declared cursor. Fields in the record and corresponding columns in the row have the same names and datatypes.
This attribute provides the datatype of a previously declared collection, cursor variable, field, object, record, database column, or variable.
This constraint prevents the assigning of nulls to a variable or constant. At run time, trying to assign a null to a variable defined as NOT NULL raises the predefined exception VALUE_ERROR. The constraint NOT NULL must be followed by an initialization clause.
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. When the declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to the constant or variable. The value and the constant or variable must have compatible datatypes.
Constants and variables are initialized every time a block or subprogram is entered. By default, variables are initialized to NULL. So, unless you expressly initialize a variable, its value is undefined.
Whether public or private, constants and variables declared in a package specification are initialized only once per session.
An initialization clause is required when declaring NOT NULL variables and when declaring constants.
You cannot use the attribute %ROWTYPE to declare a constant. If you use %ROWTYPE to declare a variable, initialization is not allowed.
Several examples of variable and constant declarations follow:
credit_limit CONSTANT NUMBER := 5000; invalid BOOLEAN := FALSE; acct_id INTEGER(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT 9999; pi CONSTANT REAL := 3.14159; last_name VARCHAR2(20); my_ename emp.ename%TYPE;
Assignment Statement, Expressions, %ROWTYPE Attribute, %TYPE Attribute
Cursors and cursor variables have four attributes that give you useful information about the execution of a data manipulation statement. For more information, see "Using Cursor Attributes".

This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable (or parameter) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This is the name of the implicit SQL cursor. For more information, see "SQL Cursor".
This is a cursor attribute, which can be appended to the name of a cursor or cursor variable. Before the first fetch from an open cursor, cursor_name%FOUND yields NULL. Thereafter, it yields TRUE if the last fetch returned a row, or FALSE if the last fetch failed to return a row.
Until a SQL statement is executed, SQL%FOUND yields NULL. Thereafter, it yields TRUE if the statement affected any rows, or FALSE if it affected no rows.
This is a cursor attribute, which can be appended to the name of a cursor or cursor variable. If a cursor is open, cursor_name%ISOPEN yields TRUE; otherwise, it yields FALSE.
Oracle automatically closes the implicit SQL cursor after executing its associated SQL statement, so SQL%ISOPEN always yields FALSE.
This is a cursor attribute, which can be appended to the name of a cursor or cursor variable. Before the first fetch from an open cursor, cursor_name%NOTFOUND yields NULL. Thereafter, it yields FALSE if the last fetch returned a row, or TRUE if the last fetch failed to return a row.
Until a SQL statement is executed, SQL%NOTFOUND yields NULL. Thereafter, it yields FALSE if the statement affected any rows, or TRUE if it affected no rows.
This is a cursor attribute, which can be appended to the name of a cursor or cursor variable. When a cursor is opened, %ROWCOUNT is zeroed. Before the first fetch, cursor_name%ROWCOUNT yields 0. Thereafter, it yields the number of rows fetched so far. The number is incremented if the latest fetch returned a row.
Until a SQL statement is executed, SQL%ROWCOUNT yields NULL. Thereafter, it yields the number of rows affected by the statement. SQL%ROWCOUNT yields 0 if the statement affected no rows.
The cursor attributes apply to every cursor or cursor variable. So, for example, you can open multiple cursors, then use %FOUND or %NOTFOUND to tell which cursors have rows left to fetch. Likewise, you can use %ROWCOUNT to tell how many rows have been fetched so far.
If a cursor or cursor variable is not open, referencing it with %FOUND, %NOTFOUND, or %ROWCOUNT raises the predefined exception INVALID_CURSOR.
When a cursor or cursor variable is opened, the rows that satisfy the associated query are identified and form the result set. Rows are fetched from the result set one at a time.
If a SELECT INTO statement returns more than one row, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception TOO_MANY_ROWS and sets %ROWCOUNT to 1, not the actual number of rows that satisfy the query.
Before the first fetch, %NOTFOUND evaluates to NULL. So, if FETCH never executes successfully, the loop is never exited. That is because the EXIT WHEN statement executes only if its WHEN condition is true. To be safe, you might want to use the following EXIT statement instead:
EXIT WHEN c1%NOTFOUND OR ci%NOTFOUND IS NULL;
You can use the cursor attributes in procedural statements but not in SQL statements.
The PL/SQL block below uses %FOUND to select an action. The IF statement either inserts a row or exits the loop unconditionally.
-- available online in file 'examp12' DECLARE CURSOR num1_cur IS SELECT num FROM num1_tab ORDER BY sequence; CURSOR num2_cur IS SELECT num FROM num2_tab ORDER BY sequence; num1 num1_tab.num%TYPE; num2 num2_tab.num%TYPE; pair_num NUMBER := 0; BEGIN OPEN num1_cur; OPEN num2_cur; LOOP -- loop through the two tables and get pairs of numbers FETCH num1_cur INTO num1; FETCH num2_cur INTO num2; IF (num1_cur%FOUND) AND (num2_cur%FOUND) THEN pair_num := pair_num + 1; INSERT INTO sum_tab VALUES (pair_num, num1 + num2); ELSE EXIT; END IF; END LOOP; CLOSE num1_cur; CLOSE num2_cur; END;
The next example uses the same block. However, instead of using %FOUND in an IF statement, it uses %NOTFOUND in an EXIT WHEN statement.
-- available online in file 'examp13' DECLARE CURSOR num1_cur IS SELECT num FROM num1_tab ORDER BY sequence; CURSOR num2_cur IS SELECT num FROM num2_tab ORDER BY sequence; num1 num1_tab.num%TYPE; num2 num2_tab.num%TYPE; pair_num NUMBER := 0; BEGIN OPEN num1_cur; OPEN num2_cur; LOOP -- loop through the two tables and get -- pairs of numbers FETCH num1_cur INTO num1; FETCH num2_cur INTO num2; EXIT WHEN (num1_cur%NOTFOUND) OR (num2_cur%NOTFOUND); pair_num := pair_num + 1; INSERT INTO sum_tab VALUES (pair_num, num1 + num2); END LOOP; CLOSE num1_cur; CLOSE num2_cur; END;
In the following example, you use %ISOPEN to make a decision:
IF NOT (emp_cur%ISOPEN) THEN OPEN emp_cur; END IF; FETCH emp_cur INTO emp_rec;
The following PL/SQL block uses %ROWCOUNT to fetch the names and salaries of the five highest-paid employees:
-- available online in file 'examp14' DECLARE CURSOR c1 is SELECT ename, empno, sal FROM emp ORDER BY sal DESC; -- start with highest-paid employee my_ename CHAR(10); my_empno NUMBER(4); my_sal NUMBER(7,2); BEGIN OPEN c1; LOOP FETCH c1 INTO my_ename, my_empno, my_sal; EXIT WHEN (c1%ROWCOUNT > 5) OR (c1%NOTFOUND); INSERT INTO temp VALUES (my_sal, my_empno, my_ename); COMMIT; END LOOP; CLOSE c1; END;
In the final example, you use %ROWCOUNT to raise an exception if an unexpectedly high number of rows is deleted:
DELETE FROM accts WHERE status = 'BAD DEBT'; IF SQL%ROWCOUNT > 10 THEN RAISE out_of_bounds; END IF;
Cursors, Cursor Variables
To execute a multi-row query, Oracle opens an unnamed work area that stores processing information. To access the information, you can use an explicit cursor, which names the work area. Or, you can use a cursor variable, which points to the work area. Whereas a cursor always refers to the same query work area, a cursor variable can refer to different work areas. To create cursor variables, you define a REF CURSOR type, then declare cursor variables of that type.
Cursor variables are like C or Pascal pointers, which hold the memory location (address) of some item instead of the item itself. So, declaring a cursor variable creates a pointer, not an item. For more information, see "Using Cursor Variables".
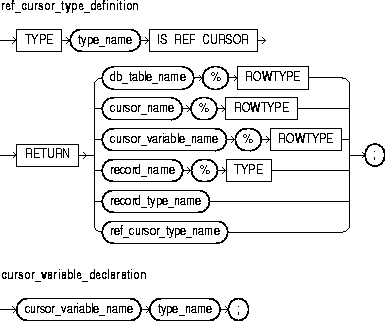
This is a user-defined type specifier, which is used in subsequent declarations of PL/SQL cursor variables.
In PL/SQL, pointers have datatype REF X, where REF is short for REFERENCE and X stands for a class of objects. Therefore, cursor variables have datatype REF CURSOR.
This keyword introduces the RETURN clause, which specifies the datatype of a cursor variable result value. You can use the %ROWTYPE attribute in the RETURN clause to provide a record type that represents a row in a database table or a row returned by a cursor or strongly typed cursor variable. Also, you can use the %TYPE attribute to provide the datatype of a previously declared record.
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a user-defined record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a RECORD type previously defined within the current scope.
This identifies a database table (or view) that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
This attribute provides a record type that represents a row in a database table or a row fetched from a cursor or strongly typed cursor variable. Fields in the record and corresponding columns in the row have the same names and datatypes.
This attribute provides the datatype of a previously declared user-defined record.
Cursor variables are available to every PL/SQL client. For example, you can declare a cursor variable in a PL/SQL host environment such as an OCI or Pro*C program, then pass it as a bind variable to PL/SQL. Moreover, application development tools such as Oracle Forms and Oracle Reports, which have a PL/SQL engine, can use cursor variables entirely on the client side.
The Oracle server also has a PL/SQL engine. So, you can pass cursor variables back and forth between an application and server via remote procedure calls (RPCs). And, if you have a PL/SQL engine on the client side, calls from client to server impose no restrictions. For example, you can declare a cursor variable on the client side, open and fetch from it on the server side, then continue to fetch from it back on the client side.
Mainly, you use cursor variables to pass query result sets between PL/SQL stored subprograms and various clients. Neither PL/SQL nor any of its clients owns a result set; they simply share a pointer to the query work area in which the result set is stored. For example, an OCI client, Oracle Forms application, and Oracle server can all refer to the same work area.
REF CURSOR types can be strong (restrictive) or weak (nonrestrictive). A strong REF CURSOR type definition specifies a return type, but a weak definition does not. Strong REF CURSOR types are less error prone because the PL/SQL compiler lets you associate a strongly typed cursor variable only with type-compatible queries. However, weak REF CURSOR types are more flexible because the compiler lets you associate a weakly typed cursor variable with any query.
Once you define a REF CURSOR type, you can declare cursor variables of that type. Yu can use %TYPE to provide the datatype of a record variable. Also, in the RETURN clause of a REF CURSOR type definition, you can use %ROWTYPE to specify a record type that represents a row returned by a strongly (not weakly) typed cursor variable.
You use three statements to control a cursor variable: OPEN-FOR, FETCH, and CLOSE. First, you OPEN a cursor variable FOR a multi-row query. Then, you FETCH rows from the result set one at a time. When all the rows are processed, you CLOSE the cursor variable.
Other OPEN-FOR statements can open the same cursor variable for different queries. You need not close a cursor variable before reopening it. When you reopen a cursor variable for a different query, the previous query is lost.
PL/SQL makes sure the return type of the cursor variable is compatible with the INTO clause of the FETCH statement. For each column value returned by the query associated with the cursor variable, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible field or variable in the INTO clause. Also, the number of fields or variables must equal the number of column values. Otherwise, you get an error.
If both cursor variables involved in an assignment are strongly typed, they must have the same datatype. However, if one or both cursor variables are weakly typed, they need not have the same datatype.
When declaring a cursor variable as the formal parameter of a subprogram that fetches from or closes the cursor variable, you must specify the IN (or IN OUT) mode. If the subprogram opens the cursor variable, you must specify the IN OUT mode.
Be careful when passing cursor variables as parameters. At run time, PL/SQL raises ROWTYPE_MISMATCH if the return types of the actual and formal parameters are incompatible.
You can apply the cursor attributes %FOUND, %NOTFOUND, %ISOPEN, and %ROWCOUNT to a cursor variable. For more information, see "Using Cursor Attributes".
If you try to fetch from, close, or apply cursor attributes to a cursor variable that does not point to a query work area, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception INVALID_CURSOR. You can make a cursor variable (or parameter) point to a query work area in two ways:
OPEN the cursor variable FOR the query.
OPENed host cursor variable or PL/SQL cursor variable.
A query work area remains accessible as long as any cursor variable points to it. Therefore, you can pass the value of a cursor variable freely from one scope to another. For example, if you pass a host cursor variable to a PL/SQL block embedded in a Pro*C program, the work area to which the cursor variable points remains accessible after the block completes.
Currently, cursor variables are subject to the following restrictions, some of which future releases of PL/SQL will remove:
OPEN-FOR statement cannot be FOR UPDATE.
REF CURSOR types to specify column types in a CREATE TABLE or CREATE VIEW statement. So, database columns cannot store the values of cursor variables.
REF CURSOR type to specify the element type of a collection, which means that elements in a collection cannot store the values of cursor variables.
You can declare a cursor variable in a PL/SQL host environment such as an OCI or Pro*C program. To use the host cursor variable, you must pass it as a bind variable to PL/SQL. In the following Pro*C example, you pass a host cursor variable and selector to a PL/SQL block, which opens the cursor variable for the chosen query:
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION; ... /* Declare host cursor variable. */ SQL_CURSOR generic_cv; int choice; EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION; ... /* Initialize host cursor variable. */ EXEC SQL ALLOCATE :generic_cv; ... /* Pass host cursor variable and selector to PL/SQL block. */ EXEC SQL EXECUTE BEGIN IF :choice = 1 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; ELSIF :choice = 2 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; ELSIF :choice = 3 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; END IF; END; END-EXEC;
Host cursor variables are compatible with any query return type. They behave just like weakly typed PL/SQL cursor variables.
When passing host cursor variables to PL/SQL, you can reduce network traffic by grouping OPEN-FOR statements. For example, the following PL/SQL block opens three cursor variables in a single round-trip:
/* anonymous PL/SQL block in host environment */ BEGIN OPEN :emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; OPEN :dept_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; OPEN :grade_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; END;
You can also pass a cursor variable to PL/SQL by calling a stored procedure that declares a cursor variable as one of its formal parameters. To centralize data retrieval, you can group type-compatible queries in a packaged procedure, as the following example shows:
CREATE PACKAGE emp_data AS TYPE EmpCurTyp IS REF CURSOR RETURN emp%ROWTYPE; PROCEDURE open_emp_cv (emp_cv IN OUT EmpCurTyp, choice IN NUMBER); END emp_data; CREATE PACKAGE BODY emp_data AS PROCEDURE open_emp_cv (emp_cv IN OUT EmpCurTyp, choice IN NUMBER) IS BEGIN IF choice = 1 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE comm IS NOT NULL; ELSIF choice = 2 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE sal > 2500; ELSIF choice = 3 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE deptno = 20; END IF; END open_emp_cv; END emp_data;
Alternatively, you can use a stand-alone procedure to open the cursor variable. Simply define the REF CURSOR type in a separate package, then reference that type in the stand-alone procedure. For instance, if you create the following (bodiless) package, you can create stand-alone procedures that reference the types it defines:
CREATE PACKAGE cv_types AS TYPE EmpCurTyp IS REF CURSOR RETURN emp%ROWTYPE; TYPE DeptCurTyp IS REF CURSOR RETURN dept%ROWTYPE; TYPE BonusCurTyp IS REF CURSOR RETURN bonus%ROWTYPE; ... END cv_types;
CLOSE Statement, Cursor Attributes, Cursors, FETCH Statement, OPEN-FOR Statement
To execute a multi-row query, Oracle opens an unnamed work area that stores processing information. A cursor lets you name the work area, access the information, and process the rows individually. For more information, see "Managing Cursors".
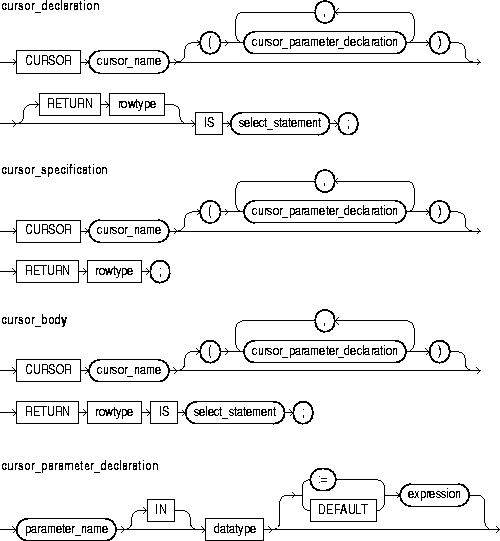
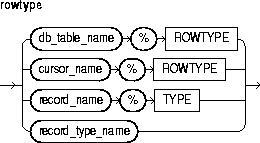
This is a query that returns a result set of rows. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement". If the cursor declaration declares parameters, each parameter must be used in the query.
This keyword introduces the RETURN clause, which specifies the datatype of a cursor result value. You can use the %ROWTYPE attribute in the RETURN clause to provide a record type that represents a row in a database table or a row returned by a previously declared cursor. Also, you can use the %TYPE attribute to provide the datatype of a previously declared record.
A cursor body must have a SELECT statement and the same RETURN clause as its corresponding cursor specification. Also, the number, order, and datatypes of select items in the SELECT clause must match the RETURN clause.
This identifies a cursor parameter; that is, a variable declared as the formal parameter of a cursor. A cursor parameter can appear in a query wherever a constant can appear. The formal parameters of a cursor must be IN parameters. The query can also reference other PL/SQL variables within its scope.
This identifies a database table (or view) that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a user-defined record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a RECORD type previously defined within the current scope.
This attribute provides a record type that represents a row in a database table or a row fetched from a previously declared cursor. Fields in the record and corresponding columns in the row have the same names and datatypes.
This attribute provides the datatype of a previously declared collection, cursor variable, field, object, record, database column, or variable.
This is a type specifier. For the syntax of datatype, see "Constants and Variables".
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. When the declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to the parameter. The value and the parameter must have compatible datatypes.
You must declare a cursor before referencing it in an OPEN, FETCH, or CLOSE statement. And, you must declare a variable before referencing it in a cursor declaration. The word SQL is reserved by PL/SQL for use as the default name for implicit cursors and cannot be used in a cursor declaration.
You cannot assign values to a cursor name or use it in an expression. However, cursors and variables follow the same scoping rules. For more information, see "Scope and Visibility".
You retrieve data from a cursor by opening it, then fetching from it. Because the FETCH statement specifies the target variables, using an INTO clause in the SELECT statement of a cursor_declaration is redundant and invalid.
The scope of cursor parameters is local to the cursor, meaning that they can be referenced only within the query used in the cursor declaration. The values of cursor parameters are used by the associated query when the cursor is opened. The query can also reference other PL/SQL variables within its scope.
The datatype of a cursor parameter must be specified without constraints. For example, the following parameter declarations are illegal:
CURSOR c1 (emp_id NUMBER NOT NULL, dept_no NUMBER(2)) -- illegal
Some examples of cursor declarations follow:
CURSOR c1 IS SELECT empno, ename, job, sal FROM emp WHERE sal > 2000; CURSOR c2 RETURN dept%ROWTYPE IS SELECT * FROM dept WHERE deptno = 10; CURSOR c3 (start_date DATE) IS SELECT empno, sal FROM emp WHERE hiredate > start_date;
CLOSE Statement, FETCH Statement, OPEN Statement, SELECT INTO Statement
The DELETE statement removes entire rows of data from a specified table or view. For a full description of the DELETE statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
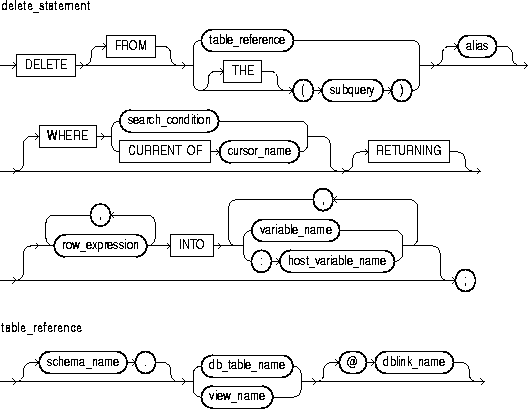
This specifies a table or view, which must be accessible when you execute the DELETE statement, and for which you must have DELETE privileges.
The operand of THE is a subquery that returns a single column value to the DELETE statement. The column value must be a nested table. Operator THE informs Oracle that the value is a nested table, not a scalar value.
This is a select statement that provides a value or set of values to the DELETE statement. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement".
This is another (usually short) name for the referenced table or view and is typically used in the WHERE clause.
This clause conditionally chooses rows to be deleted from the referenced table or view. Only rows that meet the search condition are deleted. If you omit the WHERE clause, all rows in the table or view are deleted.
This clause refers to the latest row processed by the FETCH statement associated with the cursor identified by cursor_name. The cursor must be FOR UPDATE and must be open and positioned on a row. If the cursor is not open, the CURRENT OF clause causes an error.
If the cursor is open, but no rows have been fetched or the last fetch returned no rows, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception NO_DATA_FOUND.
This clause lets you return values from the deleted row, thereby eliminating the need to SELECT the row beforehand. You can retrieve the column values into variables and/or host variables.
You can use the DELETE WHERE CURRENT OF statement after a fetch from an open cursor (this includes implicit fetches executed in a cursor FOR loop), provided the associated query is FOR UPDATE. This statement deletes the current row; that is, the one just fetched.
The implicit SQL cursor and the cursor attributes %NOTFOUND, %FOUND, and %ROWCOUNT let you access useful information about the execution of a DELETE statement.
A DELETE statement might delete one or more rows or no rows. If one or more rows are deleted, you get the following results:
If no rows are deleted, you get these results:
The following statement deletes from the bonus table all employees whose sales were below quota:
DELETE FROM bonus WHERE sales_amt < quota;
The following statement returns column sal from deleted rows and stores the column values in the elements of a host array:
DELETE FROM emp WHERE job = `CLERK' AND sal > 3000 RETURNING sal INTO :clerk_sals;
FETCH Statement, SELECT Statement
The pragma EXCEPTION_INIT associates an exception name with an Oracle error number. That allows you to refer to any internal exception by name and to write a specific handler for it instead of using the OTHERS handler. For more information, see "Using EXCEPTION_INIT".
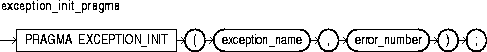
This keyword signifies that the statement is a pragma (compiler directive). Pragmas are processed at compile time, not at run time. They do not affect the meaning of a program; they simply convey information to the compiler.
This identifies a user-defined exception previously declared within the current scope.
This is any valid Oracle error number. These are the same error numbers returned by the function SQLCODE.
You can use EXCEPTION_INIT in the declarative part of any PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. The pragma must appear in the same declarative part as its associated exception, somewhere after the exception declaration.
Be sure to assign only one exception name to an error number.
The following pragma associates the exception deadlock_detected with Oracle error 60:
DECLARE deadlock_detected EXCEPTION; PRAGMA EXCEPTION_INIT(deadlock_detected, -60); BEGIN ... EXCEPTION WHEN deadlock_detected THEN -- handle the error ... END;
Exceptions, SQLCODE Function
An exception is a runtime error or warning condition, which can be predefined or user-defined. Predefined exceptions are raised implicitly (automatically) by the runtime system. User-defined exceptions must be raised explicitly by RAISE statements. To handle raised exceptions, you write separate routines called exception handlers. For more information, see Chapter 6.

This keyword introduces an exception handler. You can have multiple exceptions execute the same sequence of statements by following the keyword WHEN with a list of the exceptions, separating them by the keyword OR. If any exception in the list is raised, the associated statements are executed.
This identifies a predefined exception such as ZERO_DIVIDE, or a user-defined exception previously declared within the current scope.
This keyword stands for all the exceptions not explicitly named in the exception-handling part of the block. The use of OTHERS is optional and is allowed only as the last exception handler. You cannot include OTHERS in a list of exceptions following the keyword WHEN.
This is an executable statement. For the syntax of statement, see "Blocks".
An exception declaration can appear only in the declarative part of a block, subprogram, or package. The scope rules for exceptions and variables are the same. But, unlike variables, exceptions cannot be passed as parameters to subprograms.
Some exceptions are predefined by PL/SQL. For a list of these exceptions, see "Predefined Exceptions". PL/SQL declares predefined exceptions globally in package STANDARD, so you need not declare them yourself.
Redeclaring predefined exceptions is error prone because your local declaration overrides the global declaration. In such cases, you must use dot notation to specify the predefined exception, as follows:
EXCEPTION WHEN invalid_number OR STANDARD.INVALID_NUMBER THEN ...
The exception-handling part of a PL/SQL block is optional. Exception handlers must come at the end of the block. They are introduced by the keyword EXCEPTION. The exception-handling part of the block is terminated by the same keyword END that terminates the entire block.
An exception should be raised only when an error occurs that makes it impossible or undesirable to continue processing. If there is no exception handler in the current block for a raised exception, the exception propagates according to the following rules:
However, exceptions cannot propagate across remote procedure calls (RPCs). Therefore, a PL/SQL block cannot catch an exception raised by a remote subprogram. For a workaround, see "Using raise_application_error".
Only one exception at a time can be active in the exception-handling part of a block. Therefore, if an exception is raised inside a handler, the block that encloses the current block is the first block searched to find a handler for the newly raised exception. From there on, the exception propagates normally.
An exception handler can reference only those variables that the current block can reference.
The following PL/SQL block has two exception handlers:
DELARE bad_emp_id EXCEPTION; bad_acct_no EXCEPTION; ... BEGIN ... EXCEPTION WHEN bad_emp_id OR bad_acct_no THEN -- user-defined ROLLBACK; WHEN ZERO_DIVIDE THEN -- predefined INSERT INTO inventory VALUES (part_number, quantity); COMMIT; END;
Blocks, EXCEPTION_INIT Pragma, RAISE Statement
You use the EXIT statement to exit a loop. The EXIT statement has two forms: the unconditional EXIT and the conditional EXIT WHEN. With either form, you can name the loop to be exited. For more information, see "Iterative Control: LOOP and EXIT Statements".
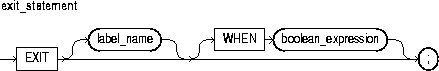
An unconditional EXIT statement (that is, one without a WHEN clause) exits the current loop immediately. Execution resumes with the statement following the loop.
This identifies the loop to be exited. You can exit not only the current loop but any enclosing labeled loop.
This is an expression that yields the Boolean value TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. It is evaluated with each iteration of the loop in which the EXIT WHEN statement appears. If the expression yields TRUE, the current loop (or the loop labeled by label_name) is exited immediately. For the syntax of boolean_expression, see "Expressions".
The EXIT statement can be used only inside a loop. PL/SQL allows you to code an infinite loop. For example, the following loop will never terminate normally:
WHILE TRUE LOOP ... END LOOP;
In such cases, you must use an EXIT statement to exit the loop.
If you use an EXIT statement to exit a cursor FOR loop prematurely, the cursor is closed automatically. The cursor is also closed automatically if an exception is raised inside the loop.
The EXIT statement in the following example is illegal because you cannot exit from a block directly; you can exit only from a loop:
DECLARE amount NUMBER; maximum NUMBER; BEGIN ... BEGIN ... IF amount >= maximum THEN EXIT; -- illegal END IF; END;
The following loop normally executes ten times, but it will exit prematurely if there are less than ten rows to fetch:
FOR i IN 1..10 FETCH c1 INTO emp_rec; EXIT WHEN c1%NOTFOUND; total_comm := total_comm + emp_rec.comm; END LOOP;
The following example illustrates the use of loop labels:
<<outer>> FOR i IN 1..10 LOOP ... <<inner>> FOR j IN 1..100 LOOP ... EXIT outer WHEN ... -- exits both loops END LOOP inner; END LOOP outer;
Expressions, LOOP Statements
An expression is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression is a single variable.
The PL/SQL compiler determines the datatype of an expression from the types of the variables, constants, literals, and operators that comprise the expression. Every time the expression is evaluated, a single value of that type results. For more information, see "Expressions and Comparisons".
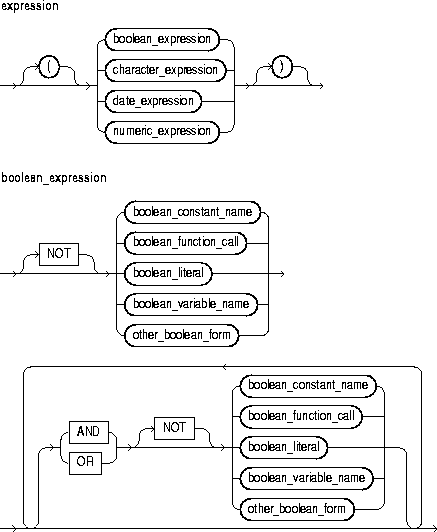
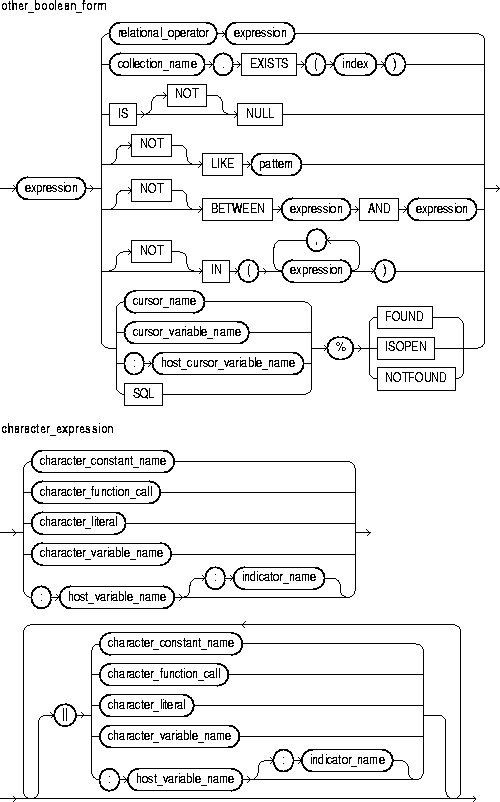
This is an expression that yields the Boolean value TRUE, FALSE, or NULL.
This is an expression that yields a character or character string.
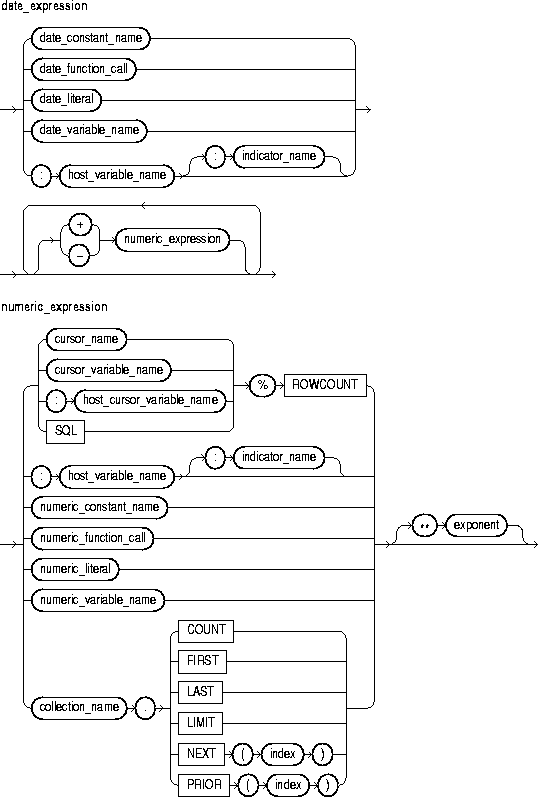
This is an expression that yields a date/time value.
This is an expression that yields an integer or real value.
These are logical operators, which follow the tri-state logic of Table 2-3. AND returns the value TRUE only if both its operands are true. OR returns the value TRUE if either of its operands is true. NOT returns the opposite value (logical negation) of its operand. NOT NULL returns NULL because nulls are indeterminate. For more information, see "Logical Operators".
This identifies a constant of type BOOLEAN, which must be initialized to the value TRUE or FALSE or the non-value NULL. Arithmetic operations on Boolean constants are illegal.
This is any function call that returns a Boolean value.
This is the predefined value TRUE or FALSE or the non-value NULL, which stands for a missing, unknown, or inapplicable value. You cannot insert the value TRUE or FALSE into a database column.
This identifies a variable of type BOOLEAN. Only the values TRUE and FALSE and the non-value NULL can be assigned to a BOOLEAN variable. You cannot select or fetch column values into a BOOLEAN variable. Also, arithmetic operations on Boolean variables are illegal.
This operator allows you to compare expressions. For the meaning of each operator, see "Comparison Operators".
This comparison operator returns the Boolean value TRUE if its operand is null, or FALSE if its operand is not null.
This comparison operator compares a character value to a pattern. Case is significant. LIKE returns the Boolean value TRUE if the character patterns match, or FALSE if they do not match.
This is a character string compared by the LIKE operator to a specified string value. It can include two special-purpose characters called wildcards. An underscore (_) matches exactly one character; a percent sign (%) matches zero or more characters.
This comparison operator tests whether a value lies in a specified range. It means "greater than or equal to low value and less than or equal to high value."
This comparison operator tests set membership. It means "equal to any member of." The set can contain nulls, but they are ignored. Also, expressions of the form
value NOT IN set
yield FALSE if the set contains a null.
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. Host cursor variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This identifies a cursor opened implicitly by Oracle to process a SQL data manipulation statement. The implicit SQL cursor always refers to the most recently executed SQL statement.
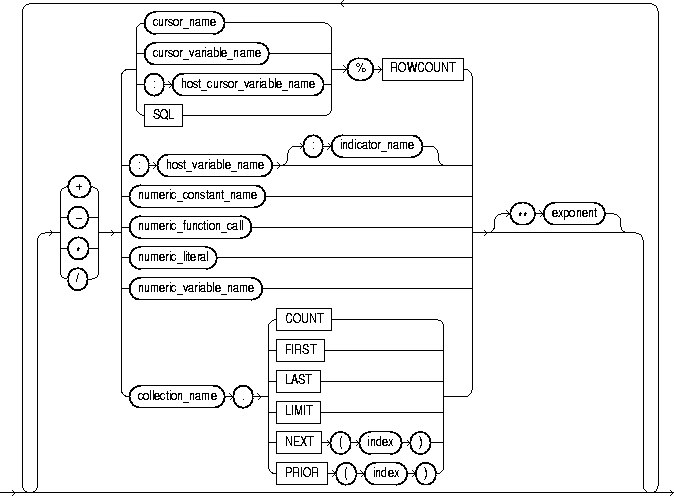
These are cursor attributes. When appended to the name of a cursor or cursor variable, these attributes return useful information about the execution of a multi-row query. You can also append them to the implicit SQL cursor. For more information, see "Using Cursor Attributes".
These are collection methods. When appended to the name of a collection, these methods return useful information. For example, EXISTS(n) returns TRUE if the nth element of a collection exists. Otherwise, EXISTS(n) returns FALSE. For more information, see "Collection Methods".
This is a numeric expression that must yield a value of type BINARY_INTEGER or a value implicitly convertible to that datatype.
This identifies a variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host variable must be implicitly convertible to the appropriate PL/SQL datatype. Also, host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This identifies an indicator variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL. Indicator variables must be prefixed with a colon. An indicator variable "indicates" the value or condition of its associated host variable. For example, in the Oracle Precompiler environment, indicator variables can detect nulls or truncated values in output host variables.
This identifies a previously declared constant that stores a numeric value. It must be initialized to a numeric value or a value implicitly convertible to a numeric value.
This is a function call that returns a numeric value or a value implicitly convertible to a numeric value.
This is a literal that represents a numeric value or a value implicitly convertible to a numeric value.
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a previously declared variable that stores a numeric value.
This keyword represents a null; it stands for a missing, unknown, or inapplicable value. When NULL is used in a numeric or date expression, the result is a null.
This is an expression that must yield a numeric value.
These symbols are the addition, subtraction, division, multiplication, and exponentiation operators, respectively.
This identifies a previously declared constant that stores a character value. It must be initialized to a character value or a value implicitly convertible to a character value.
This is a function call that returns a character value or a value implicitly convertible to a character value.
This is a literal that represents a character value or a value implicitly convertible to a character value.
This identifies a previously declared variable that stores a character value.
This is the concatenation operator. As the following example shows, the result of concatenating string1 with string2 is a character string that contains string1 followed by string2:
'Good' || ' morning!' = 'Good morning!'
The next example shows that nulls have no effect on the result of a concatenation:
'suit' || NULL || 'case' = 'suitcase'
A string zero characters in length ('') is called a null string and is treated like a null.
This identifies a previously declared constant that stores a date value. It must be initialized to a date value or a value implicitly convertible to a date value.
This is a function call that returns a date value or a value implicitly convertible to a date value.
This is a literal that represents a date value or a value implicitly convertible to a date value.
This identifies a previously declared variable that stores a date value.
In a Boolean expression, you can only compare values that have compatible datatypes. For more information, see "Datatype Conversion".
In conditional control statements, if a Boolean expression yields TRUE, its associated sequence of statements is executed. But, if the expression yields FALSE or NULL, its associated sequence of statements is not executed.
The relational operators can be applied to operands of type BOOLEAN. By definition, TRUE is greater than FALSE. Comparisons involving nulls always yield a null. The value of a Boolean expression can be assigned only to Boolean variables, not to host variables or database columns. Also, datatype conversion to or from type BOOLEAN is not supported.
You can use the addition and subtraction operators to increment or decrement a date value, as the following examples show:
hire_date := '10-MAY-95'; hire_date := hire_date + 1; -- makes hire_date '11-MAY-95' hire_date := hire_date - 5; -- makes hire_date '06-MAY-95'
When PL/SQL evaluates a boolean expression, NOT has the highest precedence, AND has the next-highest precedence, and OR has the lowest precedence. However, you can use parentheses to override the default operator precedence.
Within an expression, operations occur in their predefined order of precedence. From first to last (top to bottom), the default order of operations is
PL/SQL evaluates operators of equal precedence in no particular order. When parentheses enclose an expression that is part of a larger expression, PL/SQL evaluates the parenthesized expression first, then uses the result value in the larger expression. When parenthesized expressions are nested, PL/SQL evaluates the innermost expression first and the outermost expression last.
Several examples of expressions follow:
(a + b) > c -- Boolean expression NOT finished -- Boolean expression TO_CHAR(acct_no) -- character expression 'Fat ' || 'cats' -- character expression '15-NOV-95' -- date expression MONTHS_BETWEEN(d1, d2) -- date expression pi * r**2 -- numeric expression emp_cv%ROWCOUNT -- numeric expression
Assignment Statement, Constants and Variables, EXIT Statement, IF Statement, LOOP Statements
An external procedure is a third-generation-language routine stored in a dynamic link library (or shared library that loads dynamically), registered with PL/SQL, and called by you to do special-purpose processing. At run time, PL/SQL loads the library dynamically, then calls the routine as if it were a PL/SQL subprogram. To safeguard your database, the routine runs in a separate address space.
A dynamic link library (DLL) is an operating-system file that stores external procedures. For safety, your DBA controls access to the DLL. Using the CREATE LIBRARY statement, the DBA creates a schema object called an alias library, which represents the DLL. Then, if you are an authorized user, the DBA grants you EXECUTE privileges on the alias library. After registering an external procedure, you can call it from any PL/SQL program. It executes with the privileges granted to your userid. For more information, see Chapter 10.

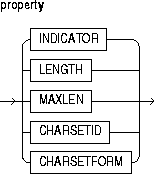
This clause specifies the name of the alias library. The name is a PL/SQL identifier. So, if you enclose the name in double quotes, it becomes case sensitive. You must have EXECUTE privileges on the alias library.
This clause specifies the external procedure to be called. If you enclose the procedure name in double quotes, it becomes case sensitive. If you omit this clause, the procedure name defaults to the upper case name of the PL/SQL subprogram.
This clause specifies the third-generation language in which the external procedure was written. Currently, the only language name allowed is C. If you omit this clause, the language name defaults to C.
This clause specifies the Windows NT calling standard (C or Pascal) under which the external procedure was compiled. (Under the Pascal Calling Standard, arguments are reversed on the stack and the called function must pop the stack.) If you omit this clause, the calling standard defaults to C.
This clause specifies that a context pointer will be passed to the external procedure. The context data structure is opaque to the external procedure but is available to service routines called by the external procedure.
By including the WITH CONTEXT clause, you can give an external procedure access to information about parameters, exceptions, memory allocation, and the user environment.
This clause specifies the positions and datatypes of parameters passed to the external procedure. It can also specify parameter properties such as current length and maximum length, and the preferred parameter passing method (by value or by reference).
You do not pass parameters to an external procedure directly. Instead, you pass them to the PL/SQL subprogram that registered the external procedure. So, you must specify PL/SQL datatypes for the parameters. For guidance, see Table 10-1. Each PL/SQL datatype maps to a default external datatype. (In turn, each external datatype maps to a C datatype.)
To avoid errors when declaring C prototype parameters, refer to Table 10-2, which shows the C datatype to specify for a given external datatype and PL/SQL parameter mode.
You can also use the PARAMETERS clause to pass additional information about PL/SQL formal parameters and function results to an external procedure. You do that by specifying the following properties: INDICATOR, LENGTH, MAXLEN, CHARSETID, CHARSETFORM.
This parameter cannot be repeated. If you include the WITH CONTEXT and PARAMETERS clauses, you must specify this parameter, which shows the position of the context pointer in the parameter list. If you omit the PARAMETERS clause, the context pointer is the first parameter passed to the external procedure.
This property lets you associate a null/not null indicator with a formal parameter. If the PL/SQL subprogram is a function, you can also associate an indicator with the return value.
These properties let you specify parameters that store the current length and maximum length of a formal parameter. With parameters of type RAW or LONG RAW, you must use the property LENGTH.
The properties CHARSETID and CHARSETFORM identify the nondefault character set from which the character data being passed was formed. With CHAR, CLOB, and VARCHAR2 parameters, you can use CHARSETID and CHARSETFORM to pass the character set ID and form to the external procedure. The OCI attribute names for these properties are OCI_ATTR_CHARSET_ID and OCI_ATTR_CHARSET_FORM.
In C, you can pass IN parameters by value (the value of the parameter is passed) or by reference (a pointer to the value is passed). When an external procedure expects a pointer, BY REF lets you pass the parameter by reference.
When calling external procedures, never write to IN parameters or overflow the capacity of OUT parameters. (PL/SQL does no runtime checks for these error conditions.) Likewise, never read an OUT parameter or a function result. Also, always assign a value to IN OUT and OUT parameters and to function results. Otherwise, your external procedure will not return successfully.
If you include the WITH CONTEXT and PARAMETERS clauses, you must specify the parameter CONTEXT, which shows the position of the context pointer in the parameter list. If you omit the PARAMETERS clause, the context pointer is the first parameter passed to the external procedure.
If you include the PARAMETERS clause and the external routine is a function, you must specify the parameter RETURN (not RETURN property) in the last position.
For every formal parameter, there must be a corresponding parameter in the PARAMETERS clause. Also, make sure that the datatypes of parameters in the PARAMETERS clause are compatible with those in the C prototype because no implicit conversions are done.
To check the value of an indicator, you can use the constants OCI_IND_NULL and OCI_IND_NOTNULL. If the indicator equals OCI_IND_NULL, the associated parameter or function result is null. If the indicator equals OCI_IND_NOTNULL, the parameter or function result is not null.
With a parameter of type RAW or LONG RAW, you must use the property LENGTH. Also, if that parameter is IN OUT or OUT and null, you must set the length of the corresponding C parameter to zero.
Currently, the following restrictions apply to external procedures:
LIBRARY clause, you cannot use a database link to specify a remote library.
Assume that C routine c_gcd, which finds the greatest common divisor of two numbers, is stored in DLL utils.dll and that you have EXECUTE privileges on alias library c_utils. The C prototype for c_gcd follows:
int c_gcd(int x_val, int y_val);
In the following example, you write a PL/SQL stand-alone function named gcd that registers the C routine c_gcd as an external function:
CREATE FUNCTION gcd ( -- find greatest common divisor of x and y x BINARY_INTEGER, y BINARY_INTEGER) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER AS EXTERNAL LIBRARY c_utils NAME "c_gcd" -- quotes preserve lower case LANGUAGE C;
In the example below, you call PL/SQL function gcd from an anonymous block. PL/SQL passes the two integer parameters to external function c_gcd, which returns their greatest common divisor.
DECLARE g INTEGER; a INTEGER; b INTEGER; ... BEGIN ... g := gcd(a, b); -- call function IF g IN (2,4,8) THEN ...
The following example uses the PARAMETERS clause to specify properties for the PL/SQL formal parameters and function result:
CREATE FUNCTION parse ( x IN BINARY_INTEGER, Y IN OUT CHAR) RETURN CHAR AS EXTERNAL LIBRARY c_utils NAME "c_parse" LANGUAGE C CALLING STANDARD PASCAL PARAMETERS ( x, -- stores value of x x INDICATOR, -- stores null status of x y, -- stores value of y y LENGTH, -- stores current length of y y MAXLEN, -- stores maximum length of y RETURN INDICATOR, RETURN);
The corresponding C prototype follows:
char * c_parse(int x, short x_ind, char *y, int *y_len, int *y_maxlen, short *retind);
Functions, Procedures
The FETCH statement retrieves rows of data one at a time from the result set of a multi-row query. The data is stored in variables or fields that correspond to the columns selected by the query. For more information, see "Managing Cursors".

This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable (or parameter) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a cursor variable declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This identifies a list of previously declared scalar variables into which column values are fetched. For each column value returned by the query associated with the cursor or cursor variable, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible variable in the list.
This identifies a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record into which rows of values are fetched. For each column value returned by the query associated with the cursor or cursor variable, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible field in the record.
You must use either a cursor FOR loop or the FETCH statement to process a multi-row query.
Any variables in the WHERE clause of the query are evaluated only when the cursor or cursor variable is opened. To change the result set or the values of variables in the query, you must reopen the cursor or cursor variable with the variables set to their new values.
To reopen a cursor, you must close it first. However, you need not close a cursor variable before reopening it.
You can use different INTO lists on separate fetches with the same cursor or cursor variable. Each fetch retrieves another row and assigns values to the target variables.
If you FETCH past the last row in the result set, the values of the target fields or variables are indeterminate and the %NOTFOUND attribute yields TRUE.
PL/SQL makes sure the return type of a cursor variable is compatible with the INTO clause of the FETCH statement. For each column value returned by the query associated with the cursor variable, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible field or variable in the INTO clause. Also, the number of fields or variables must equal the number of column values.
When you declare a cursor variable as the formal parameter of a subprogram that fetches from the cursor variable, you must specify the IN (or IN OUT) mode. However, if the subprogram also opens the cursor variable, you must specify the IN OUT mode.
Eventually, the FETCH statement must fail to return a row; so when that happens, no exception is raised. To detect the failure, you must use the cursor attribute %FOUND or %NOTFOUND. For more information, see "Using Cursor Attributes".
PL/SQL raises the predefined exception INVALID_CURSOR if you try to fetch from a closed or never-opened cursor or cursor variable.
The following example shows that any variables in the query associated with a cursor are evaluated only when the cursor is opened:
DECLARE my_sal NUMBER(7,2); n INTEGER(2) := 2; CURSOR emp_cur IS SELECT n*sal FROM emp; BEGIN OPEN emp_cur; -- n equals 2 here LOOP FETCH emp_cur INTO my_sal; EXIT WHEN emp_cur%NOTFOUND; -- process the data n := n + 1; -- does not affect next FETCH; sal will be multiplied by 2 END LOOP;
In the following Pro*C example, you fetch rows from a host cursor variable into a host record (struct) named emp_rec:
/* Exit loop when done fetching. */ EXEC SQL WHENEVER NOTFOUND DO break; for (;;) { /* Fetch row into record. */ EXEC SQL FETCH :emp_cur INTO :emp_rec; }
The next example shows that you can use a different INTO clause on separate fetches with the same cursor variable. Each fetch retrieves another row from the same result set.
for (;;) { /* Fetch row from result set. */ EXEC SQL FETCH :emp_cur INTO :emp_rec1; /* Fetch next row from same result set. */ EXEC SQL FETCH :emp_cur INTO :emp_rec2; }
CLOSE Statement, Cursors, Cursor Variables, LOOP Statements, OPEN Statement, OPEN-FOR Statement
A function is a subprogram, which can take parameters and be invoked. Generally, you use a function to compute a value. A function has two parts: the specification and the body. The function specification begins with the keyword FUNCTION and ends with the RETURN clause, which specifies the datatype of the result value. Parameter declarations are optional. Functions that take no parameters are written without parentheses. The function body begins with the keyword IS and ends with the keyword END followed by an optional function name.
The function body has three parts: an optional declarative part, an executable part, and an optional exception-handling part. The declarative part contains declarations of types, cursors, constants, variables, exceptions, and subprograms. These items are local and cease to exist when you exit the function. The executable part contains statements that assign values, control execution, and manipulate Oracle data. The exception-handling part contains exception handlers, which deal with exceptions raised during execution. For more information, see "Functions".

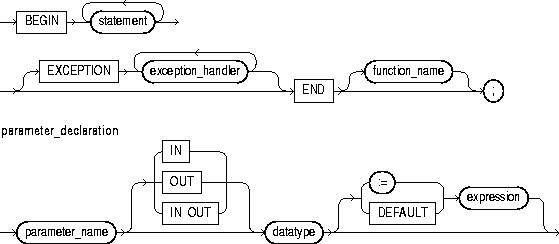
This identifies a user-defined function.
This identifies a formal parameter, which is a variable declared in a function specification and referenced in the function body.
These parameter modes define the behavior of formal parameters. An IN parameter lets you pass values to the subprogram being called. An OUT parameter lets you return values to the caller of the subprogram. An IN OUT parameter lets you pass initial values to the subprogram being called and return updated values to the caller.
This is a type specifier. For the syntax of datatype, see "Constants and Variables".
This operator or keyword allows you to initialize IN parameters to default values.
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. When the declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to the parameter. The value and the parameter must have compatible datatypes.
This keyword introduces the RETURN clause, which specifies the datatype of the result value.
This specifies a user-defined datatype. For the syntax of type_definition, see "Blocks".
This declares a program object. For the syntax of item_declaration, see "Blocks".
This construct declares a function. For the syntax of function_declaration, see "Functions".
This construct declares a procedure. For the syntax of procedure_declaration, see "Procedures".
This construct associates an exception with a sequence of statements, which is executed when that exception is raised. For the syntax of exception_handler, see "Exceptions".
A function is called as part of an expression. For example, the function sal_ok might be called as follows:
promotable := sal_ok(new_sal, new_title) AND (rating > 3);
Every function must contain at least one RETURN statement. Otherwise, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception PROGRAM_ERROR at run time.
To be callable from SQL expressions, a stored function must obey certain rules meant to control side effects. For packaged functions, you must use the pragma RESTRICT_REFERENCES to enforce the rules. For more information, see Oracle8 Application Developer's Guide.
You can write the function specification and body as a unit. Or, you can separate the function specification from its body. That way, you can hide implementation details by placing the function in a package. You can define functions in a package body without declaring their specifications in the package specification. However, such functions can be called only from inside the package.
Inside a function, an IN parameter acts like a constant. Therefore, it cannot be assigned a value. An OUT parameter acts like an uninitialized variable. So, its value cannot be assigned to another variable or reassigned to itself. An IN OUT parameter acts like an initialized variable. Therefore, it can be assigned a value, and its value can be assigned to another variable. For summary information about the parameter modes, see Table 7-1.
Avoid using the OUT and IN OUT modes with functions. The purpose of a function is to take zero or more parameters and return a single value. Also, functions should be free from side effects, which change the values of variables not local to the subprogram.
Functions can be defined using any Oracle tool that supports PL/SQL. However, to become available for general use, functions must be CREATEd and stored in an Oracle database. You can issue the CREATE FUNCTION statement interactively from SQL*Plus or Enterprise Manager. For the full syntax of the CREATE FUNCTION statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
The following function returns the balance of a specified bank account:
FUNCTION balance (acct_id INTEGER) RETURN REAL IS acct_bal REAL; BEGIN SELECT bal INTO acct_bal FROM accts WHERE acctno = acct_id; RETURN acct_bal; END balance;
Collections, Packages, Procedures, Records
The GOTO statement branches unconditionally to a statement label or block label. The label must be unique within its scope and must precede an executable statement or a PL/SQL block. The GOTO statement transfers control to the labelled statement or block. For more information, see "GOTO Statement".
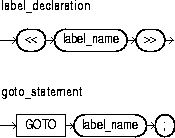
This is an undeclared identifier that labels an executable statement or a
PL/SQL block. You use a GOTO statement to transfer control to the statement or block following <<label_name>>.
Some possible destinations of a GOTO statement are illegal. In particular, a GOTO statement cannot branch into an IF statement, LOOP statement, or sub-block. For example, the following GOTO statement is illegal:
BEGIN ... GOTO update_row; -- illegal branch into IF statement ... IF valid THEN ... <<update_row>> UPDATE emp SET ... END IF;
From the current block, a GOTO statement can branch to another place in the block or into an enclosing block, but not into an exception handler. From an exception handler, a GOTO statement can branch into an enclosing block, but not into the current block.
If you use the GOTO statement to exit a cursor FOR loop prematurely, the cursor is closed automatically. The cursor is also closed automatically if an exception is raised inside the loop.
A given label can appear only once in a block. However, the label can appear in other blocks including enclosing blocks and sub-blocks. If a GOTO statement cannot find its target label in the current block, it branches to the first enclosing block in which the label appears.
A GOTO label cannot precede just any keyword. It must precede an executable statement or a PL/SQL block. For example, the following GOTO statement is illegal:
FOR ctr IN 1..50 LOOP DELETE FROM emp WHERE ... IF SQL%FOUND THEN GOTO end_loop; -- illegal END IF; ... <<end_loop>> END LOOP; -- not an executable statement
To debug the last example, simply add the NULL statement, as follows:
FOR ctr IN 1..50 LOOP DELETE FROM emp WHERE ... IF SQL%FOUND THEN GOTO end_loop; END IF; ... <<end_loop>> NULL; -- an executable statement that specifies inaction END LOOP;
For more examples of legal and illegal GOTO statements, see "GOTO Statement".
The IF statement lets you execute a sequence of statements conditionally. Whether the sequence is executed or not depends on the value of a Boolean expression. For more information, see "Conditional Control: IF Statements".
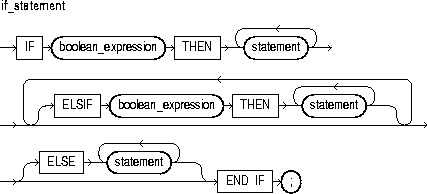
This is an expression that yields the Boolean value TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. It is associated with a sequence of statements, which is executed only if the expression yields TRUE.
This keyword associates the Boolean expression that precedes it with the sequence of statements that follows it. If the expression yields TRUE, the associated sequence of statements is executed.
This keyword introduces a Boolean expression to be evaluated if the expression following IF and all the expressions following any preceding ELSIFs yield FALSE or NULL.
If control reaches this keyword, the sequence of statements that follows it is executed.
There are three forms of IF statements: IF-THEN, IF-THEN-ELSE, and IF-THEN-ELSIF. The simplest form of IF statement associates a Boolean expression with a sequence of statements enclosed by the keywords THEN and END IF. The sequence of statements is executed only if the expression yields TRUE. If the expression yields FALSE or NULL, the IF statement does nothing. In either case, control passes to the next statement.
The second form of IF statement adds the keyword ELSE followed by an alternative sequence of statements. The sequence of statements in the ELSE clause is executed only if the Boolean expression yields FALSE or NULL. Thus, the ELSE clause ensures that a sequence of statements is executed.
The third form of IF statement uses the keyword ELSIF to introduce additional Boolean expressions. If the first expression yields FALSE or NULL, the ELSIF clause evaluates another expression. An IF statement can have any number of ELSIF clauses; the final ELSE clause is optional. Boolean expressions are evaluated one by one from top to bottom. If any expression yields TRUE, its associated sequence of statements is executed and control passes to the next statement. If all expressions yield FALSE or NULL, the sequence in the ELSE clause is executed.
An IF statement never executes more than one sequence of statements because processing is complete after any sequence of statements is executed. However, the THEN and ELSE clauses can include more IF statements. That is, IF statements can be nested.
In the example below, if shoe_count has a value of 10, both the first and second Boolean expressions yield TRUE. Nevertheless, order_quantity is assigned the proper value of 50 because processing of an IF statement stops after an expression yields TRUE and its associated sequence of statements is executed. The expression associated with ELSIF is never evaluated and control passes to the INSERT statement.
IF shoe_count < 20 THEN order_quantity := 50; ELSIF shoe_count < 30 THEN order_quantity := 20; ELSE order_quantity := 10; END IF; INSERT INTO purchase_order VALUES (shoe_type, order_quantity);
In the following example, depending on the value of score, one of two status messages is inserted into the grades table:
IF score < 70 THEN fail := fail + 1; INSERT INTO grades VALUES (student_id, 'Failed'); ELSE pass := pass + 1; INSERT INTO grades VALUES (student_id, 'Passed'); END IF;
Expressions
The INSERT statement adds new rows of data to a specified database table or view. For a full description of the INSERT statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.

This identifies a table or view that must be accessible when you execute the INSERT statement, and for which you must have INSERT privileges. For the syntax of table_reference, see "DELETE Statement".
This identifies a list of columns in a database table or view. Column names need not appear in the order in which they were defined by the CREATE TABLE or CREATE VIEW statement. However, no column name can appear more than once in the list. If the list does not include all the columns in a table, the missing columns are set to NULL or to a default value specified in the CREATE TABLE statement.
This is any expression valid in SQL. For more information, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
This clause assigns the values of expressions to corresponding columns in the column list. If there is no column list, the first value is inserted into the first column defined by the CREATE TABLE statement, the second value is inserted into the second column, and so on.
There must be only one value for each column in the column list. The first value is associated with the first column, the second value is associated with the second column, and so on. If there is no column list, you must supply a value for each column in the table.
The datatypes of the values being inserted must be compatible with the datatypes of corresponding columns in the column list.
The operand of THE is a subquery that returns a single column value to the INSERT statement. The column value must be a nested table. Operator THE informs Oracle that the value is a nested table, not a scalar value.
This is a select statement that provides a value or set of values to the INSERT statement. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement".
As many rows are added to the table as are returned by the subquery in the VALUES clause. The subquery must return a value for every column in the column list or for every column in the table if there is no column list.
This is a select statement that provides a value or set of values to the VALUES clause. The subquery must return only one row containing a value for every column in the column list or for every column in the table if there is no column list.
This clause lets you return values from the inserted row, thereby eliminating the need to SELECT the row afterward. You can retrieve the column values into variables and/or host variables.
All character and date literals in the VALUES list must be enclosed by single quotes ('). Numeric literals are not enclosed by quotes.
The implicit SQL cursor and cursor attributes %NOTFOUND, %FOUND, %ROWCOUNT, and %ISOPEN let you access useful information about the execution of an INSERT statement.
An INSERT statement might insert one or more rows or no rows. If one or more rows are inserted, you get the following results:
If no rows are inserted, you get these results:
The following examples show various forms of INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO bonus SELECT ename, job, sal, comm FROM emp WHERE comm > sal * 0.25; ... INSERT INTO emp (empno, ename, job, sal, comm, deptno) VALUES (4160, 'STURDEVIN', 'SECURITY GUARD', 2045, NULL, 30); ... INSERT INTO dept VALUES (my_deptno, UPPER(my_dname), 'CHICAGO');
SELECT Statement
A literal is an explicit numeric, character, string, or Boolean value not represented by an identifier. The numeric literal 135 and the string literal 'hello world' are examples. For more information, see "Literals".


This is an optionally signed whole number without a decimal point.
This is an optionally signed whole or fractional number with a decimal point.
This is one of the numerals 0 .. 9.
This is a member of the PL/SQL character set. For more information, see "Character Set".
This is a predefined Boolean value.
This is a predefined non-value, which stands for a missing, unknown, or inapplicable value.
Two kinds of numeric literals can be used in arithmetic expressions: integers and reals. Numeric literals must be separated by punctuation. Space characters can be used in addition to the punctuation.
A character literal is an individual character enclosed by single quotes (apostrophes). Character literals include all the printable characters in the PL/SQL character set: letters, numerals, spaces, and special symbols.
PL/SQL is case sensitive within character literals. So, for example, PL/SQL considers the literals 'Q' and 'q' to be different.
A string literal is a sequence of zero or more characters enclosed by single quotes. The null string ('') contains zero characters. To represent an apostrophe within a string, write two single quotes. PL/SQL is case sensitive within string literals. So, for example, PL/SQL considers the literals 'white' and 'White' to be different.
Also, trailing blanks are significant within string literals, so 'White' and 'White ' are different. How a string literal compares to a variable does not depend on the variable; trailing blanks in a literal are never trimmed.
Unlike the non-value NULL, the Boolean values TRUE and FALSE cannot be inserted into a database column.
Several examples of numeric literals follow:
25 6.34 7E2 25e-03 .1 1. +17 -4.4
Several examples of character literals follow:
'H' '&' ' ' '9' ']' 'g'
A few examples of string literals follow:
'$5,000' '02-AUG-87' 'Don''t leave without saving your work.'
Constants and Variables, Expressions
The LOCK TABLE statement lets you lock entire database tables in a specified lock mode so that you can share or deny access to tables while maintaining their integrity. For more information, see "Using LOCK TABLE".
This identifies a table or view that must be accessible when you execute the LOCK TABLE statement. For the syntax of table_reference, see "DELETE Statement".
This parameter specifies the lock mode. It must be one of the following: ROW SHARE, ROW EXCLUSIVE, SHARE UPDATE, SHARE, SHARE ROW EXCLUSIVE, or EXCLUSIVE.
This optional keyword tells Oracle not to wait if the table has been locked by another user. Control is immediately returned to your program, so it can do other work before trying again to acquire the lock.
If you omit the keyword NOWAIT, Oracle waits until the table is available; the wait has no set limit. Table locks are released when your transaction issues a commit or rollback.
A table lock never keeps other users from querying a table, and a query never acquires a table lock.
If your program includes SQL locking statements, make sure the Oracle users requesting locks have the privileges needed to obtain the locks. Your DBA can lock any table. Other users can lock tables they own or tables for which they have a privilege, such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
The following statement locks the accts table in shared mode:
LOCK TABLE accts IN SHARE MODE;
COMMIT Statement, ROLLBACK Statement, UPDATE Statement
LOOP statements execute a sequence of statements multiple times. The loop encloses the sequence of statements that is to be repeated. PL/SQL provides the following types of loop statements:
For more information, see "Iterative Control: LOOP and EXIT Statements".
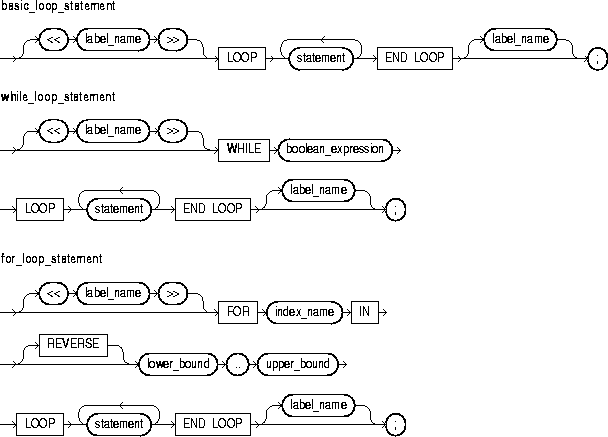
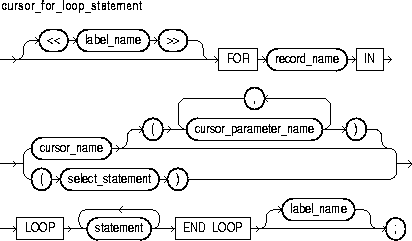
This is an undeclared identifier that optionally labels a loop. If used, label_name must be enclosed by double angle brackets and must appear at the beginning of the loop. Optionally, label_name can also appear at the end of the loop.
You can use label_name in an EXIT statement to exit the loop labelled by label_name.
You cannot reference the index of a FOR loop from a nested FOR loop if both indexes have the same name unless the outer loop is labeled by label_name and you use dot notation, as follows:
label_name.index_name
In the following example, you compare two loop indexes that have the same name, one used by an enclosing loop, the other by a nested loop:
<<outer>> FOR ctr IN 1..20 LOOP ... <<inner>> FOR ctr IN 1..10 LOOP IF outer.ctr > ctr THEN ... ... END LOOP inner; END LOOP outer;
The simplest form of LOOP statement is the basic (or infinite) loop, which encloses a sequence of statements between the keywords LOOP and END LOOP. With each iteration of the loop, the sequence of statements is executed, then control resumes at the top of the loop. If further processing is undesirable or impossible, you can use the EXIT, GOTO, or RAISE statement to complete the loop. A raised exception will also complete the loop.
The WHILE-LOOP statement associates a Boolean expression with a sequence of statements enclosed by the keywords LOOP and END LOOP. Before each iteration of the loop, the expression is evaluated. If the expression yields TRUE, the sequence of statements is executed, then control resumes at the top of the loop. If the expression yields FALSE or NULL, the loop is bypassed and control passes to the next statement.
This is an expression that yields the Boolean value TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. It is associated with a sequence of statements, which is executed only if the expression yields TRUE. For the syntax of boolean_expression, see "Expressions".
Whereas the number of iterations through a WHILE loop is unknown until the loop completes, the number of iterations through a FOR loop is known before the loop is entered. Numeric FOR loops iterate over a specified range of integers. (Cursor FOR loops, which iterate over the result set of a cursor, are discussed later.) The range is part of an iteration scheme, which is enclosed by the keywords FOR and LOOP.
The range is evaluated when the FOR loop is first entered and is never re-evaluated. The sequence of statements in the loop is executed once for each integer in the range defined by lower_bound..upper_bound. After each iteration, the loop index is incremented.
This is an undeclared identifier that names the loop index (sometimes called a loop counter). Its scope is the loop itself. Therefore, you cannot reference the index outside the loop.
The implicit declaration of index_name overrides any other declaration outside the loop. So, another variable with the same name cannot be referenced inside the loop unless a label is used, as follows:
<<main>> DECLARE num NUMBER; BEGIN ... FOR num IN 1..10 LOOP ... IF main.num > 5 THEN -- refers to the variable num, ... -- not to the loop index END IF; END LOOP; END main;
Inside a loop, its index is treated like a constant. The index can appear in expressions, but cannot be assigned a value.
These are expressions that must yield integer values. The expressions are evaluated only when the loop is first entered.
By default, the loop index is assigned the value of lower_bound. If that value is not greater than the value of upper_bound, the sequence of statements in the loop is executed, then the index is incremented. If the value of the index is still not greater than the value of upper_bound, the sequence of statements is executed again. This process repeats until the value of the index is greater than the value of upper_bound. At that point, the loop completes.
By default, iteration proceeds upward from the lower bound to the upper bound. However, if you use the keyword REVERSE, iteration proceeds downward from the upper bound to the lower bound.
An example follows:
FOR i IN REVERSE 1..10 LOOP -- i starts at 10, ends at 1 -- statements here execute 10 times END LOOP;
The loop index is assigned the value of upper_bound. If that value is not less than the value of lower_bound, the sequence of statements in the loop is executed, then the index is decremented. If the value of the index is still not less than the value of lower_bound, the sequence of statements is executed again. This process repeats until the value of the index is less than the value of lower_bound. At that point, the loop completes.
A cursor FOR loop implicitly declares its loop index as a %ROWTYPE record, opens a cursor, repeatedly fetches rows of values from the result set into fields in the record, and closes the cursor when all rows have been processed. Thus, the sequence of statements in the loop is executed once for each row that satisfies the query associated with cursor_name.
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope. When the cursor FOR loop is entered, cursor_name cannot refer to a cursor already opened by an OPEN statement or an enclosing cursor FOR loop.
This identifies an implicitly declared record. The record has the same structure as a row retrieved by cursor_name and is equivalent to a record declared as follows:
record_name cursor_name%ROWTYPE;
The record is defined only inside the loop. You cannot refer to its fields outside the loop. The implicit declaration of record_name overrides any other declaration outside the loop. So, another record with the same name cannot be referenced inside the loop unless a label is used.
Fields in the record store column values from the implicitly fetched row. The fields have the same names and datatypes as their corresponding columns. To access field values, you use dot notation, as follows:
record_name.field_name
Select-items fetched from the FOR loop cursor must have simple names or, if they are expressions, must have aliases. In the following example, wages is an alias for the select item sal+NVL(comm,0):
CURSOR c1 IS SELECT empno, sal+NVL(comm,0) wages, job ...
This identifies a cursor parameter; that is, a variable declared as the formal parameter of a cursor. A cursor parameter can appear in a query wherever a constant can appear. The formal parameters of a cursor must be IN parameters. For the syntax of cursor_parameter_declaration, see "Cursors".
This is a query associated with an internal cursor unavailable to you. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement". PL/SQL automatically declares, opens, fetches from, and closes the internal cursor. Because select_statement is not an independent statement, the implicit SQL cursor does not apply to it.
You can use the EXIT WHEN statement to exit any loop prematurely. If the Boolean expression in the WHEN clause yields TRUE, the loop is exited immediately.
When you exit a cursor FOR loop, the cursor is closed automatically even if you use an EXIT or GOTO statement to exit the loop prematurely. The cursor is also closed automatically if an exception is raised inside the loop.
The following cursor FOR loop calculates a bonus, then inserts the result into a database table:
DECLARE bonus REAL; CURSOR c1 IS SELECT empno, sal, comm FROM emp; BEGIN FOR c1rec IN c1 LOOP bonus := (c1rec.sal * 0.05) + (c1rec.comm * 0.25); INSERT INTO bonuses VALUES (c1rec.empno, bonus); END LOOP; COMMIT; END;
Cursors, EXIT Statement, FETCH Statement, OPEN Statement, %ROWTYPE Attribute
The NULL statement explicitly specifies inaction; it does nothing other than pass control to the next statement. In a construct allowing alternative actions, the NULL statement serves as a placeholder. For more information, see "NULL Statement".

The NULL statement improves readability by making the meaning and action of conditional statements clear. It tells readers that the associated alternative has not been overlooked, but that indeed no action is necessary.
Each clause in an IF statement must contain at least one executable statement. The NULL statement meets this requirement. So, you can use the NULL statement in clauses that correspond to circumstances in which no action is taken. The NULL statement and Boolean non-value NULL are unrelated.
In the following example, the NULL statement emphasizes that only salespeople receive commissions:
IF job_title = 'SALESPERSON' THEN compute_commission(emp_id); ELSE NULL; END IF;
In the next example, the NULL statement shows that no action is taken for unnamed exceptions:
EXCEPTION ... WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL;
An object type is a user-defined composite datatype that encapsulates a data structure along with the functions and procedures needed to manipulate the data. The variables that form the data structure are called attributes. The functions and procedures that characterize the behavior of the object type are called methods.
Currently, you cannot define object types within PL/SQL. They must be CREATEd and stored in an Oracle database, where they can be shared by many programs. When you define an object type (in SQL*Plus for example) using the CREATE TYPE statement, you create an abstract template for some real-world object. The template specifies only those attributes and behaviors the object will need in the application environment.
The data structure formed by the set of attributes is public (visible to client programs). However, well-behaved programs do not manipulate it directly. Instead, they use the set of methods provided. That way, the data is kept in a proper state. At run time, when the data structure is filled with values, you have created an instance of an object type. You can create as many instances (usually called objects) as you need. For more information, see Chapter 9.
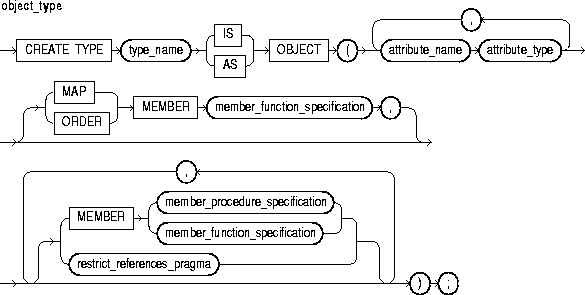
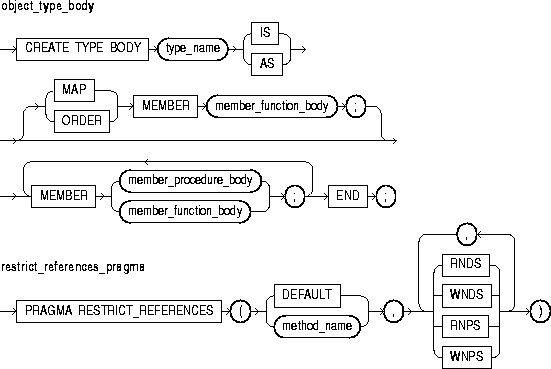
This identifies a user-defined type specifier, which is used in subsequent declarations of objects.
This identifies an object attribute. The name must be unique within the object type (but can be reused in other object types). You cannot initialize an attribute in its declaration using the assignment operator or DEFAULT clause. Also, you cannot impose the NOT NULL constraint on an attribute.
This is any Oracle datatype except LONG, LONG RAW, MLSLABEL, NCHAR, NCLOB, NVARCHAR2, ROWID, the PL/SQL-specific types BINARY_INTEGER (and its subtypes), BOOLEAN, PLS_INTEGER, RECORD, REF CURSOR, %TYPE, and %ROWTYPE, and types defined inside a PL/SQL package.
This keyword allows you to declare a function or procedure in an object type specification. The method cannot have the same name as the object type or any of its attributes.
Like packaged subprograms, methods have two parts: a specification and a body. The specification consists of a method name, an optional parameter list, and, for functions, a return type. The body is the code that executes to perform a specific operation.
For each method specification in an object type specification, there must be a corresponding method body in the object type body. To match method specifications and bodies, the compiler does a token-by-token comparison of their headers. So, the headers must match word for word.
All methods in an object type accept an instance of that type as their first parameter. The name of this built-in parameter is SELF. Whether declared implicitly or explicitly, SELF is always the first parameter passed to a method. In a method body, SELF denotes the object whose method was called.
In member functions, if SELF is not declared, its parameter mode defaults to IN. However, in member procedures, if SELF is not declared, its parameter mode defaults to IN OUT. You cannot specify a different datatype for SELF.
This keyword indicates that a method orders objects by mapping them to values of a scalar datatype such as CHAR or REAL, which have a predefined order. PL/SQL uses the ordering to evaluate Boolean expressions such as x > y, and to do comparisons implied by the DISTINCT, GROUP BY, and ORDER BY clauses. A map method returns the relative position of an object in the ordering of all such objects.
An object type can contain only one map method, which must be a parameterless function having the return type DATE, NUMBER, VARCHAR2, or an ANSI SQL type such as CHARACTER, INTEGER, or REAL.
This keyword indicates that a method compares two objects. Every order method takes just two parameters: the built-in parameter SELF and another object of the same type. If o1 and o2 are objects, a comparison such as o1 > o2 automatically calls the order method with parameters o1 and o2. The method returns a negative number, zero, or a positive number signifying that SELF is less than, equal to, or greater than the other parameter, respectively.
An object type can contain only one order method, which must be a function that returns a numeric result.
This construct declares the interface to a member function. Its syntax is like that of function_specification without the terminator. See "Functions".
This construct declares the interface to a member procedure. Its syntax is like that of procedure_specification without the terminator. See "Procedures".
This construct defines the underlying implementation of a member function. Its syntax is like that of function_body without the terminator. See "Functions".
This construct defines the underlying implementation of a member procedure. Its syntax is like that of procedure_body without the terminator. See "Procedures".
You use this pragma (compiler directive) to enforce rules that control side effects. The pragma tells the PL/SQL compiler to deny the member function read/write access to database tables, packaged variables, or both.
In the object type specification, you code the pragma somewhere after the method to which it applies. You can specify up to four constraints in any order, but you must specify WNDS. To call the method from parallel queries, you must also specify WNPS, RNDS, and RNPS. No constraint implies another.
If you specify the keyword DEFAULT instead of a method name, the pragma applies to all member functions including the system-defined constructor. You can declare the pragma for any member function. Such pragmas override the default pragma. However, a non-default pragma can apply to only one method. So, among overloaded methods, the pragma always applies to the nearest preceding method.
Once an object type is defined and installed in the schema, you can use it to declare objects in any PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. For example, you can use the object type to specify the datatype of an attribute, column, variable, bind variable, record field, table element, formal parameter, or function result.
Like a package, an object type has two parts: a specification and a body. The specification is the interface to your applications; it declares a data structure (set of attributes) along with the operations (methods) needed to manipulate the data. The body fully defines the methods, and so implements the specification.
All the information a client program needs to use the methods is in the specification. Think of the specification as an operational interface and of the body as a black box. You can debug, enhance, or replace the body without changing the specification.
An object type encapsulates data and operations. So, you can declare attributes and methods in an object type specification, but not constants, exceptions, cursors, or types. At least one attribute is required; methods are optional.
In an object type specification, all attributes must be declared before any methods. Only subprograms have an underlying implementation. So, if an object type specification declares only attributes, the object type body is unnecessary. You cannot declare attributes in the body.
All declarations in the object type specification are public (visible outside the object type). However, the object type body can contain private declarations, which define methods necessary for the internal workings of the object type. The scope of private declarations is local to the object type body.
You can refer to an attribute only by name (not by its position in the object type). To access or change the value of an attribute, you use dot notation. Attribute names can be chained, which allows you to access the attributes of a nested object type.
In an object type, methods can reference attributes and other methods without a qualifier. In SQL statements, calls to a parameterless method require an empty parameter list. In procedural statements, an empty parameter list is optional unless you chain calls, in which case it is required for all but the last call.
You can declare a map method or an order method but not both. If you declare either method, you can compare objects in SQL and procedural statements. However, if you declare neither method, you can compare objects only in SQL statements and only for equality or inequality. Two objects of the same type are equal only if the values of their corresponding attributes are equal.
Like packaged subprograms, methods of the same kind (functions or procedures) can be overloaded. That is, you can use the same name for different methods if their formal parameters differ in number, order, or datatype family.
Every object type has a constructor method (constructor for short), which is a system-defined function with the same name as the object type. You use the constructor to initialize and return an instance of that object type. PL/SQL never calls a constructor implicitly, so you must call it explicitly. Constructor calls are allowed wherever function calls are allowed.
In the SQL*Plus script below, an object type for a stack is defined. The last item added to a stack is the first item removed. The operations push and pop update the stack while preserving last in, first out (LIFO) behavior. The simplest implementation of a stack uses an integer array. Integers are stored in array elements, with one end of the array representing the top of the stack.
CREATE TYPE IntArray AS VARRAY(25) OF INTEGER / CREATE TYPE Stack AS OBJECT ( max_size INTEGER, top INTEGER, position IntArray, MEMBER PROCEDURE initialize, MEMBER FUNCTION full RETURN BOOLEAN, MEMBER FUNCTION empty RETURN BOOLEAN, MEMBER PROCEDURE push (n IN INTEGER), MEMBER PROCEDURE pop (n OUT INTEGER) ) / CREATE TYPE BODY Stack AS MEMBER PROCEDURE initialize IS -- fill stack with nulls BEGIN top := 0; -- call constructor for varray and set element 1 to NULL position := IntArray(NULL); max_size := position.LIMIT; -- use varray size constraint (25) position.EXTEND(max_size - 1, 1); -- copy element 1 into 2..25 END initialize; MEMBER FUNCTION full RETURN BOOLEAN IS -- return TRUE if stack is full BEGIN RETURN (top = max_size); END full; MEMBER FUNCTION empty RETURN BOOLEAN IS -- return TRUE if stack is empty BEGIN RETURN (top = 0); END empty; MEMBER PROCEDURE push (n IN INTEGER) IS -- push integer onto stack BEGIN IF NOT full THEN top := top + 1; position(top) := n; ELSE -- stack is full RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20101, `stack overflow'); END IF; END push; MEMBER PROCEDURE pop (n OUT INTEGER) IS -- pop integer off stack and return its value BEGIN IF NOT empty THEN n := position(top); top := top - 1; ELSE -- stack is empty RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20102, `stack underflow'); END IF; END pop; END;
Notice that in member procedures push and pop, we use the built-in procedure raise_application_error to issue user-defined error messages. That way, we can report errors to the client program and avoid returning unhandled exceptions to the host environment.
The following example shows that you can nest object types:
CREATE TYPE Address AS OBJECT ( street_address VARCHAR2(35), city VARCHAR2(15), state CHAR(2), zip_code INTEGER ); CREATE TYPE Person AS OBJECT ( first_name VARCHAR2(15), last_name VARCHAR2(15), birthday DATE, home_address Address, -- nested object type phone_number VARCHAR2(15), ss_number INTEGER, );
Functions, Packages, Procedures
The OPEN statement executes the multi-row query associated with an explicit cursor. It also allocates resources used by Oracle to process the query and identifies the result set, which consists of all rows that meet the query search criteria. The cursor is positioned before the first row in the result set. For more information, see "Managing Cursors".
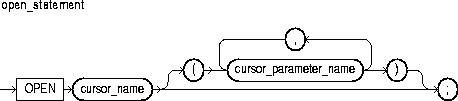
This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope and not currently open.
This identifies a cursor parameter; that is, a variable declared as the formal parameter of a cursor. A cursor parameter can appear in a query wherever a constant can appear. For the syntax of cursor_parameter_ declaration, see "Cursors".
Generally, PL/SQL parses an explicit cursor only the first time it is opened and parses a SQL statement (thereby creating an implicit cursor) only the first time the statement is executed. All the parsed SQL statements are cached. A SQL statement must be reparsed only if it is bumped out of the cache by a new SQL statement.
So, although you must close a cursor before you can reopen it, PL/SQL need not reparse the associated SELECT statement. If you close, then immediately reopen the cursor, a reparse is definitely not needed.
Rows in the result set are not retrieved when the OPEN statement is executed. The FETCH statement retrieves the rows. With a FOR UPDATE cursor, the rows are locked when the cursor is opened.
If formal parameters are declared, actual parameters must be passed to the cursor. The formal parameters of a cursor must be IN parameters. Therefore, they cannot return values to actual parameters. The values of actual parameters are used when the cursor is opened. The datatypes of the formal and actual parameters must be compatible. The query can also reference PL/SQL variables declared within its scope.
Unless you want to accept default values, each formal parameter in the cursor declaration must have a corresponding actual parameter in the OPEN statement. Formal parameters declared with a default value need not have a corresponding actual parameter. They can simply assume their default values when the OPEN statement is executed.
You can associate the actual parameters in an OPEN statement with the formal parameters in a cursor declaration using positional or named notation. For more information, see "Positional and Named Notation".
If a cursor is currently open, you cannot use its name in a cursor FOR loop.
Given the cursor declaration
CURSOR parts_cur IS SELECT part_num, part_price FROM parts;
the following statement opens the cursor:
OPEN parts_cur;
Given the cursor declaration
CURSOR emp_cur(my_ename CHAR, my_comm NUMBER DEFAULT 0) IS SELECT * FROM emp WHERE ...
any of the following statements opens the cursor:
OPEN emp_cur('LEE'); OPEN emp_cur('BLAKE', 300); OPEN emp_cur(employee_name, 150);
CLOSE Statement, Cursors, FETCH Statement, LOOP Statements
The OPEN-FOR statement executes the multi-row query associated with a cursor variable. It also allocates resources used by Oracle to process the query and identifies the result set, which consists of all rows that meet the query search criteria. The cursor variable is positioned before the first row in the result set. For more information, see "Using Cursor Variables".
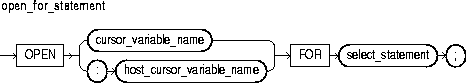
This identifies a cursor variable (or parameter) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a cursor variable previously declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. The datatype of the host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Host variables must be prefixed with a colon.
This is a query associated with cursor_variable, which returns a set of values. The query can reference bind variables and PL/SQL variables, parameters, and functions but cannot be FOR UPDATE. The syntax of select_statement is similar to the syntax for select_into_statement defined in "SELECT INTO Statement", except that select_statement cannot have an INTO clause.
You can declare a cursor variable in a PL/SQL host environment such as an OCI or Pro*C program. To open the host cursor variable, you can pass it as a bind variable to an anonymous PL/SQL block. You can reduce network traffic by grouping OPEN-FOR statements. For example, the following PL/SQL block opens five cursor variables in a single round-trip:
/* anonymous PL/SQL block in host environment */ BEGIN OPEN :emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; OPEN :dept_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; OPEN :grade_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; OPEN :pay_cv FOR SELECT * FROM payroll; OPEN :ins_cv FOR SELECT * FROM insurance; END;
Other OPEN-FOR statements can open the same cursor variable for different queries. You need not close a cursor variable before reopening it. When you reopen a cursor variable for a different query, the previous query is lost.
Unlike cursors, cursor variables do not take parameters. No flexibility is lost, however, because you can pass whole queries (not just parameters) to a cursor variable.
You can pass a cursor variable to PL/SQL by calling a stored procedure that declares a cursor variable as one of its formal parameters. However, remote subprograms on another server cannot accept the values of cursor variables. Therefore, you cannot use a remote procedure call (RPC) to open a cursor variable.
When you declare a cursor variable as the formal parameter of a subprogram that opens the cursor variable, you must specify the IN OUT mode. That way, the subprogram can pass an open cursor back to the caller.
In the following Pro*C example, you pass a host cursor variable and selector to a PL/SQL block, which opens the cursor variable for the chosen query:
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION; ... /* Declare host cursor variable. */ SQL_CURSOR generic_cv; int choice; EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION; ... /* Initialize host cursor variable. */ EXEC SQL ALLOCATE :generic_cv; ... /* Pass host cursor variable and selector to PL/SQL block. */ EXEC SQL EXECUTE BEGIN IF :choice = 1 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; ELSIF :choice = 2 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; ELSIF :choice = 3 THEN OPEN :generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; END IF; END; END-EXEC;
To centralize data retrieval, you can group type-compatible queries in a stored procedure. When called, the following packaged procedure opens the cursor variable emp_cv for the chosen query:
CREATE PACKAGE emp_data AS TYPE GenericCurTyp IS REF CURSOR; TYPE EmpCurTyp IS REF CURSOR RETURN emp%ROWTYPE; PROCEDURE open_emp_cv (emp_cv IN OUT EmpCurTyp, choice IN NUMBER); END emp_data; CREATE PACKAGE BODY emp_data AS PROCEDURE open_emp_cv (emp_cv IN OUT EmpCurTyp, choice IN NUMBER) IS BEGIN IF choice = 1 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE comm IS NOT NULL; ELSIF choice = 2 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE sal > 2500; ELSIF choice = 3 THEN OPEN emp_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp WHERE deptno = 20; END IF; END open_emp_cv; END emp_data;
For more flexibility, you can pass a cursor variable to a stored procedure that executes queries with different return types, as follows:
CREATE PACKAGE BODY emp_data AS PROCEDURE open_cv (generic_cv IN OUT GenericCurTyp, choice IN NUMBER) IS BEGIN IF choice = 1 THEN OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; ELSIF choice = 2 THEN OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; ELSIF choice = 3 THEN OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; END IF; END open_cv; END emp_data;
CLOSE Statement, Cursor Variables, FETCH Statement, LOOP Statements
A package is a schema object that groups logically related PL/SQL types, items, and subprograms. Packages have two parts: a specification and a body. For more information, see Chapter 8.

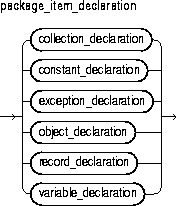
This identifies a package. For naming conventions, see "Identifiers".
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope. For the syntax of collection_declaration, see "Collections".
This construct declares a constant. For the syntax of constant_declaration, see "Constants and Variables".
This construct declares an exception. For the syntax of exception_declaration, see "Exceptions".
This identifies an object (instance of an object type) previously declared within the current scope. For the syntax of object_declaration, see "Object Types".
This construct declares a user-defined record. For the syntax of record_declaration, see "Records".
This construct declares a variable. For the syntax of variable_declaration, see "Constants and Variables".
This construct declares the interface to an explicit cursor. For the syntax of cursor_specification, see "Cursors".
This construct declares the interface to a function. For the syntax of function_specification, see "Functions".
This construct declares the interface to a procedure. For the syntax of procedure_specification, see "Procedures".
This construct defines the underlying implementation of an explicit cursor. For the syntax of cursor_body, see "Cursors".
This construct defines the underlying implementation of a function. For the syntax of function_body, see "Functions".
This construct defines the underlying implementation of a procedure. For the syntax of procedure_body, see "Procedures".
You cannot define packages in a PL/SQL block or subprogram. However, you can use any Oracle tool that supports PL/SQL to create and store packages in an Oracle database. You can issue the CREATE PACKAGE and CREATE PACKAGE BODY statements interactively from SQL*Plus or Enterprise Manager and from an Oracle Precompiler or OCI host program. For the full syntax of the CREATE PACKAGE statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
Most packages have a specification and a body. The specification is the interface to your applications; it declares the types, variables, constants, exceptions, cursors, and subprograms available for use. The body fully defines cursors and subprograms, and so implements the specification.
Only subprograms and cursors have an underlying implementation (definition). So, if a specification declares only types, constants, variables, and exceptions, the package body is unnecessary. However, the body can still be used to initialize items declared in the specification, as the following example shows:
CREATE PACKAGE emp_actions AS ... number_hired INTEGER; END emp_actions; CREATE PACKAGE BODY emp_actions AS BEGIN number_hired := 0; END emp_actions;
You can code and compile a specification without its body. Once the specification has been compiled, stored subprograms that reference the package can be compiled as well. You need not define the package bodies fully until you are ready to complete the application.
Furthermore, you can debug, enhance, or replace a package body without changing the interface (package specification) to the package body. That means you need not recompile calling programs.
Cursors and subprograms declared in a package specification must be defined in the package body. Other program items declared in the package specification cannot be redeclared in the package body.
To match subprogram specifications and bodies, PL/SQL does a token-by-token comparison of their headers. So, except for white space, the headers must match word for word. Otherwise, PL/SQL raises an exception.
Collections, Cursors, Exceptions, Functions, Procedures, Records
A procedure is a subprogram, which can take parameters and be invoked. Generally, you use a procedure to perform an action. A procedure has two parts: the specification and the body. The procedure specification begins with the keyword PROCEDURE and ends with the procedure name or a parameter list. Parameter declarations are optional. Procedures that take no parameters are written without parentheses. The procedure body begins with the keyword IS and ends with the keyword END followed by an optional procedure name.
The procedure body has three parts: an optional declarative part, an executable part, and an optional exception-handling part. The declarative part contains declarations of types, cursors, constants, variables, exceptions, and subprograms. These items are local and cease to exist when you exit the procedure. The executable part contains statements that assign values, control execution, and manipulate Oracle data. The exception-handling part contains exception handlers, which deal with exceptions raised during execution. For more information, see "Procedures".
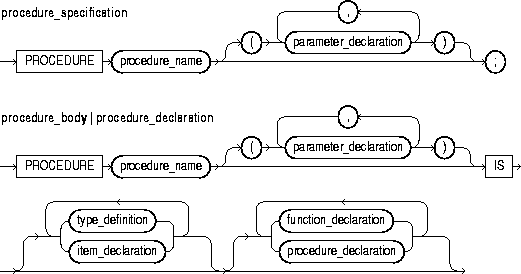
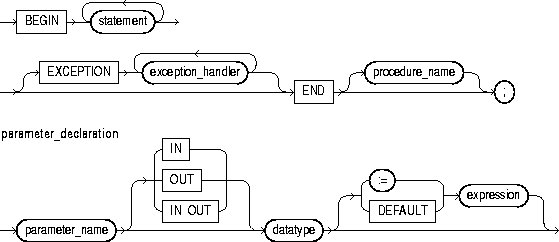
This identifies a user-defined procedure.
This identifies a formal parameter, which is a variable declared in a procedure specification and referenced in the procedure body.
These parameter modes define the behavior of formal parameters. An IN parameter lets you pass values to the subprogram being called. An OUT parameter lets you return values to the caller of the subprogram. An IN OUT parameter lets you pass initial values to the subprogram being called and return updated values to the caller.
This is a type specifier. For the syntax of datatype, see "Constants and Variables".
This operator or keyword allows you to initialize IN parameters to default values.
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. When the declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to the parameter. The value and the parameter must have compatible datatypes.
This specifies a user-defined datatype. For the syntax of type_definition, see "Blocks".
This declares a program object. For the syntax of item_declaration, see "Blocks".
This construct declares a function. For the syntax of function_declaration, see "Functions".
This construct declares a procedure. For the syntax of procedure_declaration, see "Procedures".
This construct associates an exception with a sequence of statements, which is executed when that exception is raised. For the syntax of exception_handler, see "Exceptions".
A procedure is called as a PL/SQL statement. For example, the procedure raise_salary might be called as follows:
raise_salary(emp_num, amount);
Inside a procedure, an IN parameter acts like a constant. Therefore, it cannot be assigned a value. An OUT parameter acts like an uninitialized variable. So, its value cannot be assigned to another variable or reassigned to itself. An IN OUT parameter acts like an initialized variable. Therefore, it can be assigned a value, and its value can be assigned to another variable. For summary information about the parameter modes, see Table 7-1.
Unlike OUT and IN OUT parameters, IN parameters can be initialized to default values. For more information, see "Parameter Default Values".
Before exiting a procedure, explicitly assign values to all OUT formal parameters. Otherwise, the values of corresponding actual parameters are indeterminate. If you exit successfully, PL/SQL assigns values to the actual parameters. However, if you exit with an unhandled exception, PL/SQL does not assign values to the actual parameters.
You can write the procedure specification and body as a unit. Or, you can separate the procedure specification from its body. That way, you can hide implementation details by placing the procedure in a package. You can define procedures in a package body without declaring their specifications in the package specification. However, such procedures can be called only from inside the package.
Procedures can be defined using any Oracle tool that supports PL/SQL. To become available for general use, however, procedures must be CREATEd and stored in an Oracle database. You can issue the CREATE PROCEDURE statement interactively from SQL*Plus or Enterprise Manager. For the full syntax of the CREATE PROCEDURE statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
At least one statement must appear in the executable part of a procedure. The NULL statement meets this requirement.
The following procedure debits a bank account:
PROCEDURE debit_account (acct_id INTEGER, amount REAL) IS old_balance REAL; new_balance REAL; overdrawn EXCEPTION; BEGIN SELECT bal INTO old_balance FROM accts WHERE acctno = acct_id; new_balance := old_balance - amount; IF new_balance < 0 THEN RAISE overdrawn; ELSE UPDATE accts SET bal = new_balance WHERE acctno = acct_id; END IF; EXCEPTION WHEN overdrawn THEN ... END debit_account;
In the following example, you call the procedure using named notation:
debit_account(amount => 500, acct_id => 10261);
Collections, Functions, Packages, Records
The RAISE statement stops normal execution of a PL/SQL block or subprogram and transfers control to the appropriate exception handler. Normally, predefined exceptions are raised implicitly by the runtime system. However, RAISE statements can also raise predefined exceptions. User-defined exceptions must be raised explicitly by RAISE statements. For more information, see "User-Defined Exceptions".

This identifies a predefined or user-defined exception. For a list of the predefined exceptions, see "Predefined Exceptions".
PL/SQL blocks and subprograms should RAISE an exception only when an error makes it impractical or impossible to continue processing. You can code a RAISE statement for a given exception anywhere within the scope of that exception.
When an exception is raised, if PL/SQL cannot find a handler for it in the current block, the exception propagates. That is, the exception reproduces itself in successive enclosing blocks until a handler is found or there are no more blocks to search. In the latter case, PL/SQL returns an unhandled exception error to the host environment.
Omitting the exception name in a RAISE statement, which is allowed only in an exception handler, reraises the current exception. When a parameterless RAISE statement executes in an exception handler, the first block searched is the enclosing block, not the current block.
In the following example, you raise an exception when an inventoried part is out of stock:
IF quantity_on_hand = 0 THEN RAISE out_of_stock; END IF;
Exceptions
Records are items of type RECORD. Records have uniquely named fields that can store data values of different types. For more information, see "What Is a Record?".

This identifies a user-defined type specifier, which is used in subsequent declarations of records.
This constraint prevents the assigning of nulls to a field. At run time, trying to assign a null to a field defined as NOT NULL raises the predefined exception VALUE_ERROR. The constraint NOT NULL must be followed by an initialization clause.
This is a type specifier. For the syntax of datatype, see "Constants and Variables".
This operator or keyword allows you to initialize fields to default values.
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. For the syntax of expression, see "Expressions". When the declaration is elaborated, the value of expression is assigned to the field. The value and the field must have compatible datatypes.
You can define RECORD types and declare user-defined records in the declarative part of any block, subprogram, or package. Also, a record can be initialized in its declaration, as the following example shows:
DECLARE TYPE TimeTyp IS RECORD( second SMALLINT := 0, minute SMALLINT := 0, hour SMALLINT := 0);
The next example shows that you can use the %TYPE attribute to specify a field datatype. It also shows that you can add the NOT NULL constraint to any field declaration and so prevent the assigning of nulls to that field.
DECLARE TYPE DeptRecTyp IS RECORD( deptno NUMBER(2) NOT NULL, dname dept.dname%TYPE, loc dept.loc%TYPE); dept_rec DeptRecTyp;
To reference individual fields in a record, you use dot notation. For example, you might assign a value to the dname field in the dept_rec record as follows:
dept_rec.dname := 'PURCHASING';
Instead of assigning values separately to each field in a record, you can assign values to all fields at once. This can be done in two ways. First, you can assign one user-defined record to another if they have the same datatype. (Having fields that match exactly is not enough.) You can assign a %ROWTYPE record to a user-defined record if their fields match in number and order, and corresponding fields have compatible datatypes.
Second, you can use the SELECT or FETCH statement to fetch column values into a record. The columns in the select-list must appear in the same order as the fields in your record.
You can declare and reference nested records. That is, a record can be the component of another record, as the following example shows:
DECLARE TYPE TimeTyp IS RECORD( minute SMALLINT, hour SMALLINT); TYPE MeetingTyp IS RECORD( day DATE, time TimeTyp, -- nested record place CHAR(20), purpose CHAR(50)); TYPE PartyTyp IS RECORD( day DATE, time TimeTyp, -- nested record loc CHAR(15)); meeting MeetingTyp; seminar MeetingTyp; party PartyTyp;
The next example shows that you can assign one nested record to another if they have the same datatype:
seminar.time := meeting.time;
Such assignments are allowed even if the containing records have different datatypes.
User-defined records follow the usual scoping and instantiation rules. In a package, they are instantiated when you first reference the package and cease to exist when you exit the application or end the database session. In a block or subprogram, they are instantiated when you enter the block or subprogram and cease to exist when you exit the block or subprogram.
Like scalar variables, user-defined records can be declared as the formal parameters of procedures and functions. The restrictions that apply to scalar parameters also apply to user-defined records.
You can specify a RECORD type in the RETURN clause of a function specification. That allows the function to return a user-defined record of the same type. When calling a function that returns a user-defined record, you use the following syntax to reference fields in the record:
function_name(parameters).field_name
To reference nested fields in a record returned by a function, you use the following syntax:
function_name(parameters).field_name.nested_field_name
Currently, you cannot use the syntax above to call a parameterless function because PL/SQL does not allow empty parameter lists. That is, the following syntax is illegal:
function_name().field_name -- illegal; empty parameter list
You cannot just drop the empty parameter list because the following syntax is also illegal:
function_name.field_name -- illegal; no parameter list
Instead, declare a local user-defined record to which you can assign the function result, then reference its fields directly.
In the following example, you define a RECORD type named DeptRecTyp, declare a record named dept_rec, then select a row of values into the record:
DECLARE TYPE DeptRecTyp IS RECORD( deptno NUMBER(2), dname CHAR(14), loc CHAR(13)); dept_rec DeptRecTyp; ... BEGIN SELECT deptno, dname, loc INTO dept_rec FROM dept WHERE deptno = 20;
Assignment Statement, Collections, Functions, Procedures
The RETURN statement immediately completes the execution of a subprogram and returns control to the caller. Execution then resumes with the statement following the subprogram call. In a function, the RETURN statement also sets the function identifier to the result value. For more information, see "RETURN Statement".
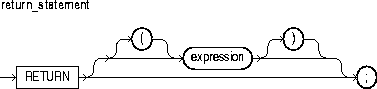
This is an arbitrarily complex combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and function calls. The simplest expression consists of a single variable. When the RETURN statement is executed, the value of expression is assigned to the function identifier.
Do not confuse the RETURN statement with the RETURN clause, which specifies the datatype of the result value in a function specification.
A subprogram can contain several RETURN statements, none of which need be the last lexical statement. Executing any of them completes the subprogram immediately. However, to have multiple exit points in a subprogram is a poor programming practice.
In procedures, a RETURN statement cannot contain an expression. The statement simply returns control to the caller before the normal end of the procedure is reached.
However, in functions, a RETURN statement must contain an expression, which is evaluated when the RETURN statement is executed. The resulting value is assigned to the function identifier. Therefore, a function must contain at least one RETURN statement. Otherwise, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception PROGRAM_ERROR at run time.
The RETURN statement can also be used in an anonymous block to exit the block (and all enclosing blocks) immediately, but the RETURN statement cannot contain an expression.
In the following example, the function balance RETURNs the balance of a specified bank account:
FUNCTION balance (acct_id INTEGER) RETURN REAL IS acct_bal REAL; BEGIN SELECT bal INTO acct_bal FROM accts WHERE acctno = acct_id; RETURN acct_bal; END balance;
Functions, Procedures
The ROLLBACK statement is the inverse of the COMMIT statement. It undoes some or all database changes made during the current transaction. For more information, see "Processing Transactions".

When a parameterless ROLLBACK statement is executed, all database changes made during the current transaction are undone.
This keyword is optional and has no effect except to improve readability.
This statement undoes all database changes (and releases all locks acquired) since the savepoint identified by savepoint_name was marked.
This keyword is optional and has no effect except to improve readability.
This is an undeclared identifier, which marks the current point in the processing of a transaction. For naming conventions, see "Identifiers".
All savepoints marked after the savepoint to which you roll back are erased. However, the savepoint to which you roll back is not erased. For example, if you mark savepoints A, B, C, and D in that order, then roll back to savepoint B, only savepoints C and D are erased.
An implicit savepoint is marked before executing an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement. If the statement fails, a rollback to the implicit savepoint is done. Normally, just the failed SQL statement is rolled back, not the whole transaction. However, if the statement raises an unhandled exception, the host environment determines what is rolled back.
COMMIT Statement, SAVEPOINT Statement
The %ROWTYPE attribute provides a record type that represents a row in a database table. The record can store an entire row of data selected from the table or fetched from a cursor or cursor variable. Fields in a record and corresponding columns in a row have the same names and datatypes.
You can use the %ROWTYPE attribute in variable declarations as a datatype specifier. Variables declared using %ROWTYPE are treated like those declared using a datatype name. For more information, see "Using %ROWTYPE".

This identifies an explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL strongly (not weakly) typed cursor variable previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a database table (or view) that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
The %ROWTYPE attribute lets you declare records structured like a row of data in a database table.
To reference a field, you use dot notation. For example, you might reference the deptno field as follows:
IF emp_rec.deptno = 20 THEN ...
You can assign the value of an expression to a specific field, as the following example shows:
emp_rec.sal := average * 1.15;
There are two ways to assign values to all fields in a record at once. First, PL/SQL allows aggregate assignment between entire records if their declarations refer to the same table or cursor.
Second, you can assign a list of column values to a record by using the SELECT or FETCH statement. The column names must appear in the order in which they were defined by the CREATE TABLE or CREATE VIEW statement. Select-items fetched from a cursor associated with %ROWTYPE must have simple names or, if they are expressions, must have aliases.
In the example below, you use %ROWTYPE to declare two records. The first record stores a row selected from the emp table. The second record stores a row fetched from the c1 cursor.
DECLARE emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE; CURSOR c1 IS SELECT deptno, dname, loc FROM dept; dept_rec c1%ROWTYPE;
In the next example, you select a row from the emp table into a %ROWTYPE record:
DECLARE emp_rec emp%ROWTYPE; ... BEGIN SELECT * INTO emp_rec FROM emp WHERE empno = my_empno; IF (emp_rec.deptno = 20) AND (emp_rec.sal > 2000) THEN ... END IF; END;
Constants and Variables, Cursors, Cursor Variables, FETCH Statement
The SAVEPOINT statement names and marks the current point in the processing of a transaction. With the ROLLBACK TO statement, savepoints let you undo parts of a transaction instead of the whole transaction. For more information, see "Processing Transactions".
This is an undeclared identifier, which marks the current point in the processing of a transaction.
When you roll back to a savepoint, any savepoints marked after that savepoint are erased. However, the savepoint to which you roll back is not erased. A simple rollback or commit erases all savepoints. Savepoint names can be reused within a transaction. This moves the savepoint from its old position to the current point in the transaction.
If you mark a savepoint within a recursive subprogram, new instances of the SAVEPOINT statement are executed at each level in the recursive descent. However, you can only roll back to the most recently marked savepoint.
An implicit savepoint is marked before executing an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement. If the statement fails, a rollback to the implicit savepoint is done. Normally, just the failed SQL statement is rolled back, not the whole transaction. However, if the statement raises an unhandled exception, the host environment determines what is rolled back.
COMMIT Statement, ROLLBACK Statement
The SELECT INTO statement retrieves data from one or more database tables, then assigns the selected values to variables or fields. For a full description of the SELECT statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.

This is a value returned by the SELECT statement, then assigned to the corresponding variable or field in the INTO clause.
This identifies a list of previously declared scalar variables into which select_item values are fetched. For each select_item value returned by the query, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible variable in the list.
This identifies a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record into which rows of values are fetched. For each select_item value returned by the query, there must be a corresponding, type-compatible field in the record.
This identifies a table or view that must be accessible when you execute the SELECT statement, and for which you must have SELECT privileges. For the syntax of table_reference, see "DELETE Statement".
The operand of THE is a subquery that returns a single column value to the SELECT statement. The column value must be a nested table. Operator THE informs Oracle that the value is a nested table, not a scalar value.
This is query that provides a value or set of values to the SELECT statement. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement".
This is another (usually short) name for the referenced column, table, or view.
This is anything that can legally follow the FROM clause in a SELECT statement.
The implicit SQL cursor and the cursor attributes %NOTFOUND, %FOUND, %ROWCOUNT, and %ISOPEN let you access useful information about the execution of a SELECT INTO statement.
When you use a SELECT INTO statement to assign values to variables, it should return only one row. If it returns more than one row, you get the following results:
TOO_MANY_ROWS
SQLCODE returns -1422 (Oracle error code ORA-01422)
SQLERRM returns the Oracle error message single-row query returns more than one row
SQL%NOTFOUND yields FALSE
SQL%FOUND yields TRUE
SQL%ROWCOUNT yields 1
If no rows are returned, you get these results:
NO_DATA_FOUND unless the SELECT statement called a SQL group function such as AVG or SUM. (SQL group functions always return a value or a null. So, a SELECT INTO statement that calls a group function never raises NO_DATA_FOUND.)
SQLCODE returns +100 (Oracle error code ORA-01403)
SQLERRM returns the Oracle error message no data found
SQL%NOTFOUND yields TRUE
SQL%FOUND yields FALSE
SQL%ROWCOUNT yields 0
The following SELECT statement returns an employee's name, job title, and salary from the emp database table:
SELECT ename, job, sal INTO my_ename, my_job, my_sal FROM emp WHERE empno = my_empno;
Assignment Statement, FETCH Statement, %ROWTYPE Attribute
The SET TRANSACTION statement begins a read-only or read-write transaction, establishes an isolation level, or assigns the current transaction to a specified rollback segment. Read-only transactions are useful for running multiple queries against one or more tables while other users update the same tables. For more information, see "Using SET TRANSACTION".

This clause establishes the current transaction as read-only. If a transaction is set to READ ONLY, subsequent queries see only changes committed before the transaction began. The use of READ ONLY does not affect other users or transactions.
This clause establishes the current transaction as read-write. The use of READ WRITE does not affect other users or transactions. If the transaction executes a data manipulation statement, Oracle assigns the transaction to a rollback segment.
This clause specifies how transactions that modify the database are handled. When you specify SERIALIZABLE, if a serializable transaction tries to execute a SQL data manipulation statement that modifies any table already modified by an uncommitted transaction, the statement fails.
To enable SERIALIZABLE mode, your DBA must set the Oracle initialization parameter COMPATIBLE to 7.3.0 or higher.
When you specify READ COMMITTED, if a transaction includes SQL data manipulation statements that require row locks held by another transaction, the statement waits until the row locks are released.
This clause assigns the current transaction to the specified rollback segment and establishes the transaction as read-write. You cannot use this parameter with the READ ONLY parameter in the same transaction because read-only transactions do not generate rollback information.
The SET TRANSACTION statement must be the first SQL statement in your transaction and can appear only once in the transaction.
In the following example, you establish a read-only transaction:
COMMIT; -- end previous transaction SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY; SELECT ... FROM emp WHERE ... SELECT ... FROM dept WHERE ... SELECT ... FROM emp WHERE ... COMMIT; -- end read-only transaction
COMMIT Statement, ROLLBACK Statement, SAVEPOINT Statement
Oracle implicitly opens a cursor to process each SQL statement not associated with an explicit cursor. PL/SQL lets you refer to the most recent implicit cursor as the SQL cursor, which has four attributes: %FOUND, %ISOPEN, %NOTFOUND, and %ROWCOUNT. They give you information about the execution of data manipulation statements. For more information, see "Managing Cursors".
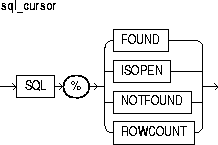
This is the name of the implicit SQL cursor.
This attribute yields TRUE if an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement affected one or more rows or a SELECT INTO statement returned one or more rows. Otherwise, it yields FALSE.
This attribute always yields FALSE because Oracle closes the SQL cursor automatically after executing its associated SQL statement.
This attribute is the logical opposite of %FOUND. It yields TRUE if an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement affected no rows, or a SELECT INTO statement returned no rows. Otherwise, it yields FALSE.
This attribute yields the number of rows affected by an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement, or returned by a SELECT INTO statement.
You can use cursor attributes in procedural statements but not in SQL statements. Before Oracle opens the SQL cursor automatically, the implicit cursor attributes yield NULL.
The values of cursor attributes always refer to the most recently executed SQL statement, wherever that statement appears. It might be in a different scope. So, if you want to save an attribute value for later use, assign it to a Boolean variable immediately.
If a SELECT INTO statement fails to return a row, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception NO_DATA_FOUND whether you check SQL%NOTFOUND on the next line or not.
However, a SELECT INTO statement that calls a SQL group function never raises NO_DATA_FOUND. That is because group functions such as AVG and SUM always return a value or a null. In such cases, SQL%NOTFOUND yields FALSE.
In the following example, %NOTFOUND is used to insert a row if an update affects no rows:
UPDATE emp SET sal = sal * 1.05 WHERE empno = my_empno; IF SQL%NOTFOUND THEN INSERT INTO emp VALUES (my_empno, my_ename, ...); END IF;
In the next example, you use %ROWCOUNT to raise an exception if more than 100 rows are deleted:
DELETE FROM parts WHERE status = 'OBSOLETE'; IF SQL%ROWCOUNT > 100 THEN -- more than 100 rows were deleted RAISE large_deletion; END IF;
Cursors, Cursor Attributes
The function SQLCODE returns the number code associated with the most recently raised exception. SQLCODE is meaningful only in an exception handler. Outside a handler, SQLCODE always returns zero.
For internal exceptions, SQLCODE returns the number of the associated Oracle error. The number that SQLCODE returns is negative unless the Oracle error is no data found, in which case SQLCODE returns +100.
For user-defined exceptions, SQLCODE returns +1 unless you used the pragma EXCEPTION_INIT to associate the exception with an Oracle error number, in which case SQLCODE returns that error number. For more information, see "Using SQLCODE and SQLERRM".

You cannot use SQLCODE directly in a SQL statement. First, you must assign the value of SQLCODE to a local variable. An example follows:
DECLARE my_sqlcode NUMBER; BEGIN ... EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN my_sqlcode := SQLCODE; INSERT INTO errors VALUES (my_sqlcode, ...); END;
SQLCODE is especially useful in the OTHERS exception handler because it lets you identify which internal exception was raised.
Exceptions, SQLERRM Function
The function SQLERRM returns the error message associated with its error-number argument or, if the argument is omitted, with the current value of SQLCODE. SQLERRM with no argument is meaningful only in an exception handler. Outside a handler, SQLERRM with no argument always returns the message normal, successful completion.
For internal exceptions, SQLERRM returns the message associated with the Oracle error that occurred. The message begins with the Oracle error code.
For user-defined exceptions, SQLERRM returns the message user-defined exception unless you used the pragma EXCEPTION_INIT to associate the exception with an Oracle error number, in which case SQLERRM returns the corresponding error message. For more information, see "Using SQLCODE and SQLERRM".

This must be a valid Oracle error number. For a list of Oracle errors, see Oracle8 Error Messages.
You can pass an error number to SQLERRM, in which case SQLERRM returns the message associated with that error number. The error number passed to SQLERRM should be negative. Passing a zero to SQLERRM always returns the following message:
ORA-0000: normal, successful completion
Passing a positive number to SQLERRM always returns the message
User-Defined Exception
unless you pass +100, in which case SQLERRM returns the following message:
ORA-01403: no data found
You cannot use SQLERRM directly in a SQL statement. First, you must assign the value of SQLERRM to a local variable. An example follows:
DECLARE my_sqlerrm CHAR(150); ... BEGIN ... EXCEPTION ... WHEN OTHERS THEN my_sqlerrm := SUBSTR(SQLERRM, 1, 150); INSERT INTO errors VALUES (my_sqlerrm, ...); END;
The string function SUBSTR ensures that a VALUE_ERROR exception (for truncation) is not raised when you assign the value of SQLERRM to my_sqlerrm. SQLERRM is especially useful in the OTHERS exception handler because it lets you identify which internal exception was raised.
Exceptions, SQLCODE Function
The %TYPE attribute provides the datatype of a field, record, nested table, database column, or variable. You can use the %TYPE attribute as a datatype specifier when declaring constants, variables, fields, and parameters. For more information, see "Using %TYPE".
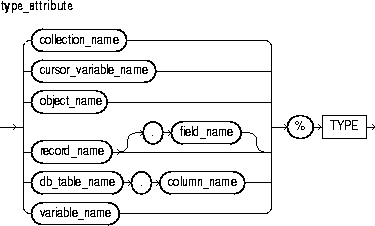
This identifies a nested table, index-by table, or varray previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope. Only the value of another cursor variable can be assigned to a cursor variable.
This identifies an object (instance of an object type) previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
This identifies a field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
This refers to a table and column that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
This is the name of a variable previously declared in the same scope.
The %TYPE attribute is particularly useful when declaring variables, fields, and parameters that refer to database columns. However, the NOT NULL column constraint does not apply to items declared using %TYPE.
Constants and Variables, %ROWTYPE Attribute
The UPDATE statement changes the values of specified columns in one or more rows in a table or view. For a full description of the UPDATE statement, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
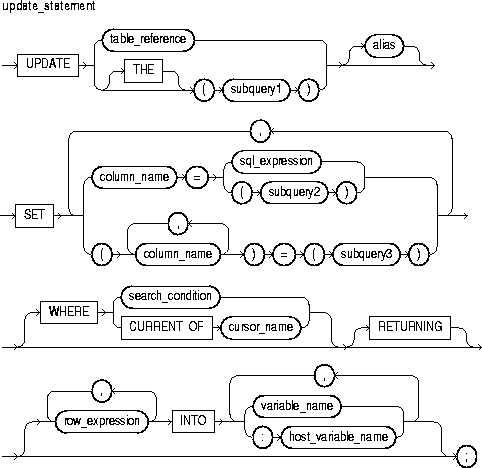
This identifies a table or view that must be accessible when you execute the UPDATE statement, and for which you must have UPDATE privileges. For the syntax of table_reference, see "DELETE Statement".
The operand of THE is a subquery that returns a single column value to the UPDATE statement. The column value must be a nested table. Operator THE informs Oracle that the value is a nested table, not a scalar value.
This is a select statement that provides a value or set of values to the UPDATE statement. Its syntax is like that of select_into_statement without the INTO clause. See "SELECT INTO Statement".
This is another (usually short) name for the referenced table or view and is typically used in the WHERE clause.
This is the name of the column (or one of the columns) to be updated. It must be the name of a column in the referenced table or view. A column name cannot be repeated in the column_name list. Column names need not appear in the UPDATE statement in the same order that they appear in the table or view.
This is any valid SQL expression. For more information, see Oracle8 SQL Reference.
This clause assigns the value of sql_expression to the column identified by column_name. If sql_expression contains references to columns in the table being updated, the references are resolved in the context of the current row. The old column values are used on the right side of the equal sign.
In the following example, you increase every employee's salary by 10%. The original value of the sal column is multiplied by 1.1, then the result is assigned to the sal column.
UPDATE emp SET sal = sal * 1.1;
This clause assigns the value retrieved from the database by subquery2 to the column identified by column_name. The subquery must return exactly one row and one column.
This clause assigns the values retrieved from the database by subquery3 to the columns in the column_name list. The subquery must return exactly one row that includes all the columns listed.
The column values returned by the subquery are assigned to the columns in the column list in order. Thus, the first value is assigned to the first column in the list, the second value is assigned to the second column in the list, and so on.
In the following correlated query, the column item_id is assigned the value stored in item_num, and the column price is assigned the value stored in item_price:
UPDATE inventory inv -- alias SET (item_id, price) = (SELECT item_num, item_price FROM item_table WHERE item_name = inv.item_name);
This clause chooses which rows to update in the database table. Only rows that meet the search condition are updated. If you omit the search condition, all rows in the table are updated.
This clause refers to the latest row processed by the FETCH statement associated with the cursor identified by cursor_name. The cursor must be FOR UPDATE and must be open and positioned on a row.
If the cursor is not open, the CURRENT OF clause causes an error. If the cursor is open, but no rows have been fetched or the last fetch returned no rows, PL/SQL raises the predefined exception NO_DATA_FOUND.
This clause lets you return values from the updated row, thereby eliminating the need to SELECT the row afterward. You can retrieve the column values into variables and/or host variables.
You can use the UPDATE WHERE CURRENT OF statement after a fetch from an open cursor (this includes implicit fetches executed in a cursor FOR loop), provided the associated query is FOR UPDATE. This statement updates the current row; that is, the one just fetched.
The implicit SQL cursor and the cursor attributes %NOTFOUND, %FOUND, %ROWCOUNT, and %ISOPEN let you access useful information about the execution of an UPDATE statement.
An UPDATE statement might update one or more rows or no rows. If one or more rows are updated, you get the following results:
If no rows are updated, you get these results:
In the following example, a 10% raise is given to all analysts and clerks in department 20:
UPDATE emp SET sal = sal * 1.10 WHERE (job = 'ANALYST' OR job = 'CLERK') AND DEPTNO = 20;
In the next example, an employee named Ford is promoted to the position of Analyst and her salary is raised by 15%:
UPDATE emp SET job = 'ANALYST', sal = sal * 1.15 WHERE ename = 'FORD';
In the final example, you return values from an updated row and store them in variables:
UPDATE emp SET sal = sal + 500 WHERE ename = 'MILLER' RETURNING sal, ename INTO my_sal, my_ename;
DELETE Statement, FETCH Statement