|
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 | |
|
Search for most updated materials ↑
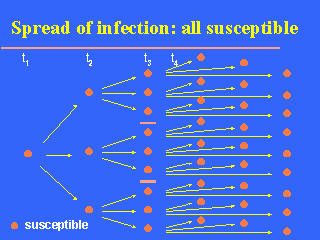
Imagine that an infected case of a directly transmitted disease is introduced in a totally susceptible population and that the biological characteristics of the microorganism (in relation to those of man) and the social conditions of the human population are such that one infected case transmits the infection to three susceptible persons on average. A simplistic representation of this situation would look like the slide. Note: t1, t2 etc. denotes successive "time periods" or "generations" or "waves" of infectious transmission.
|