|
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 | |
|
Search for most updated materials ↑
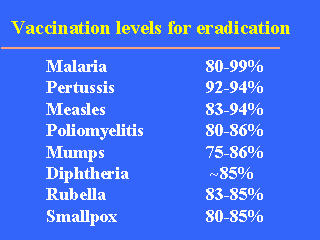
This
slide presents approximate estimates of the order of magnitude of the critical proportions
of vaccination (PC), derived from several studies. For successful eradication, these levels of vaccination coverage should be achieved in
all sectors or of the population; a national average is not enough, as the microorganism
may be sustained in "pockets" of the population where R remains >=1. MORE: Estimated values of A, L, R0 and PC for
different infections and populations. (Source of data: Fine P. Herd immunity: history, theory, practice.
Epidemiol Rev 1993;
15:265-302.)
|