|
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 | |
|
Search for most updated materials ↑
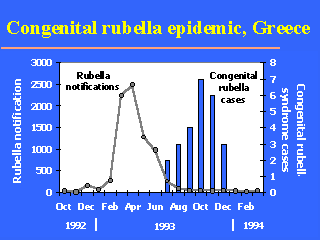
Twenty-five serologically confirmed cases
(24.6 per 100,000 live births) were recorded. This was the largest number of congenital
rubella cases that has ever been recorded in Greece. More information on the
congenital rubella epidemic of 1993 in Greece. This epidemic should serve as cautionary note on the potential hazards of the
introduction of rubella immunisation, especially in countries that may have difficulty in
assuring high vaccination coverage because of a limited tradition of public health and/or
lack of resources. (Source of data for slides 23-26: Panagiotopoulos T, Antoniadou I, Valassi-Adam E.
Increase in congenital rubella occurrence after immunisation in Greece: retrospective
survey and systematic review. BMJ 1999; 319:1462-6.)
|