| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |review |
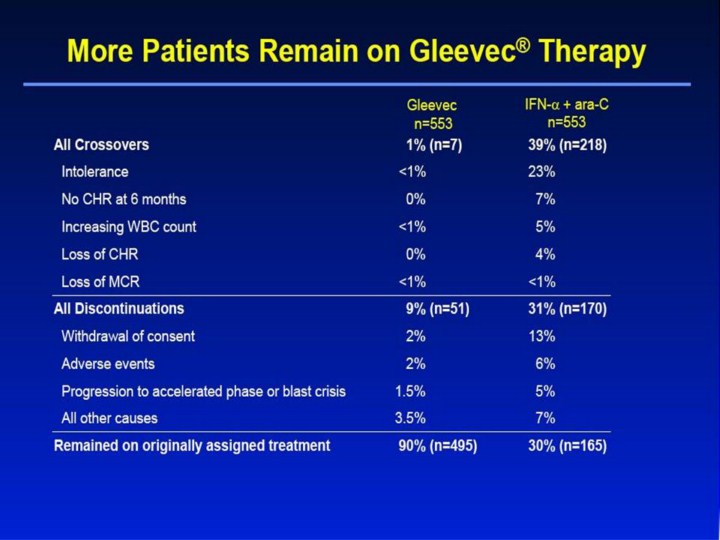 |
More Patients Remain on Gleevec® Therapy All Crossovers 1% (n=7) 39% (n=218) Intolerance <1% 23% No CHR at 6 months 0% 7% Increasing WBC count <1% 5% Loss of CHR 0% 4% Loss of MCR <1% <1% All Discontinuations 9% (n=51) 31% (n=170) Withdrawal of consent 2% 13% Adverse events 2% 6% Progression to accelerated phase or blast crisis 1.5% 5% All other causes 3.5% 7% Remained on originally assigned treatment 90% (n=495) 30% (n=165) IFN-α + ara-C n=553 Gleevec n=553 [Slide 17] More Patients Remain on Gleevec® Therapy1,2 • There was a marked difference in crossover rates between the 2 treatment arms: 39% of patients crossed over to the Gleevec arm vs only 1% of patients crossing over to the IFN-α + ara-C arm. • The primary reason for crossover in the IRIS study was intolerance of the IFN-α–based regimen (23%). • Intolerance was defined as grades 3/4 non-hematologic toxicity that persisted despite dose reduction and symptomatic therapy. • Discontinuation rates were also substantially different: 31% in the IFN-α + ara-C arm vs only 1% in the Gleevec arm. • Causes of discontinuation not shown (“All other causes”) included protocol violation, death on study, and SCT. • As a result of both crossovers and discontinuations, only 30% of patients on IFN-α + ara-C remained on their treatment vs 90% of patients remaining on Gleevec therapy. References 1. Gleevec® (imatinib mesylate) Prescribing Information. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2003. 2. Data on file. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, NJ. |